Topics
Matter
Physical Quantities and Measurement
- Measurements
- Unit and Its Types
- Unit Systems
- Physical Quantities
- Rules and Conventions for Writing SI Units and Their Symbols
- International System of Units (Si System)
- Unit Prefixes
- Measurement of Length
- Devices for Measuring Length
- Measurement of Mass
- Devices for Measuring Mass
- Measurement of Time
- Devices for Measuring Time
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Measuring Temperature
- Area and It’s Unit
- Measurement of Area
Force
- Force - Push or Pull
- Effect of Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Force of Friction
- Effects of Friction
- Kinds of Friction
- Advantages and Disadvantage of Friction
- Increasing and Reducing Friction
Energy
- Concept of Work
- Energy
- Machines
- Principle of Machine
- Efficiency of a Machine
- Simple Machines
- Mechanical Advantage
- A Lever
- Types of Levers
- A Pulley
- A Wheel and Axle
- An Inclined Plane
- A Wedge
- Screw
- Care of Machines
- Machines (Numerical)
Light
Magnetism
- Discovery of Magnets
- Classification of Magnets
- Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Magnet
- Magnetic Properties
- Magnetic Field
- Earth’s Magnetism
- Making a Magnet
- Electromagnet
- Making of an Electromagnet
- Applications of Electromagnets
- Care and Storage of Magnets
- Demagnetization of a Magnet
Introduction:
An eclipse is a natural celestial event that occurs when one astronomical object moves into the shadow of another.
- In the case of Earth, we observe two main types of eclipses: the solar eclipse and the lunar eclipse. Both phenomena happen due to the alignment of the sun, moon, and earth in a straight or nearly straight line.
- Eclipses occur because the moon revolves around the earth, and the earth, along with the moon, revolves around the sun. Since these bodies move in different orbits, they occasionally come into alignment, causing one celestial object to cast a shadow on another.
- When the earth, sun, and moon align perfectly, an eclipse occurs. This alignment is called syzygy.
There are two main shadows involved in an eclipse:
- Umbra: The darkest part of the shadow where the light source is fully blocked.
- Penumbra: The lighter, outer part of the shadow where only a part of the light is blocked.
Eclipses provide valuable opportunities for scientists to study celestial bodies and their behaviour, and they have also been subjects of fascination, myths, and legends throughout human history.
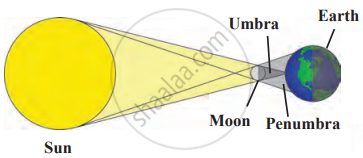
Solar Eclipse:
The moon comes between the sun and the earth, casting a shadow on part of the earth. It only occurs on a new moon day. Solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth about every 18 months and last only a few minutes. Never look directly at the sun during an eclipse-it can damage your eyes. Always use proper safety equipment to watch a solar eclipse.
Solar Eclipse
| Type | Visibility | Cause | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
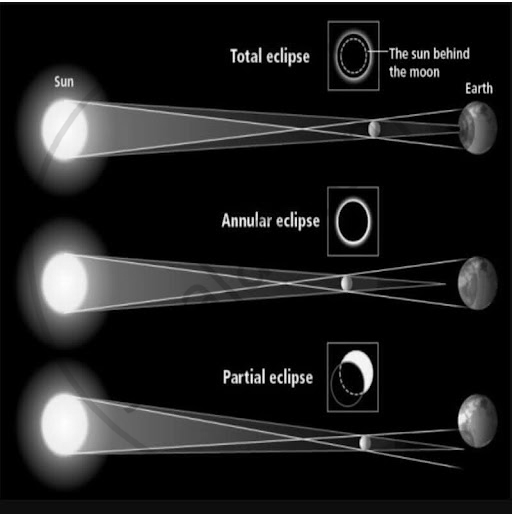
| Total Solar Eclipse | It is visible from a small area on Earth. | It occurs when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are perfectly aligned. | The sky becomes very dark, as if it were night, for those in the centre of the moon’s shadow. |
| Partial Solar Eclipse | It is visible when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are not aligned. | The moon covers only a small part of the sun’s surface. | A dark shadow appears on the part of the Sun. |
| Annular Solar Eclipse | Occurs when the Moon is at its farthest distance from Earth. | The Moon looks smaller and cannot cover the entire Sun. | A ring of sunlight appears around the moon, creating a bright "ring of fire" effect. |
The Moon’s Shadow on Earth:
- Umbra: The darkest part of the moon’s shadow. People standing in the umbra will see a total eclipse.
- Penumbra: The lighter outer part of the shadow. People in the penumbra will see a partial eclipse.
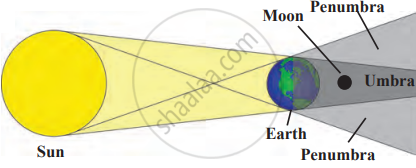
Lunar Eclipse:
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, blocking the Sun’s light that usually makes the Moonshine. Instead of sunlight reaching the moon, Earth’s shadow falls on it. Lunar eclipses only occur during a full moon and last for a few hours. At least two partial lunar eclipses occur every year, but total lunar eclipses are rare. It is safe to watch a lunar eclipse without any eye protection.
Lunar Eclipse
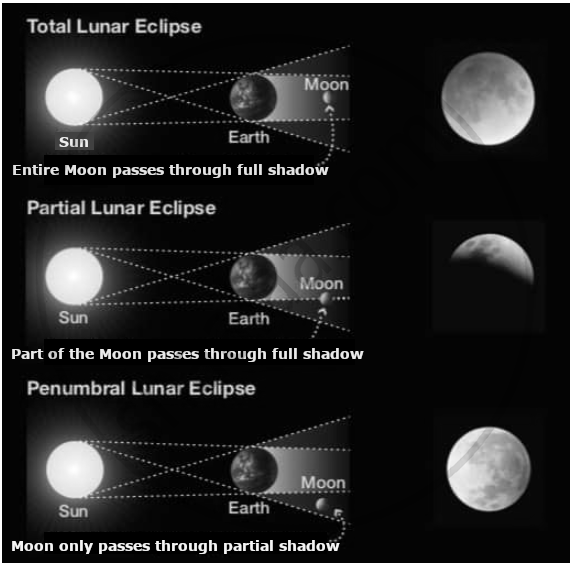

| Type | Cause | Visibility | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Lunar Eclipse | The Moon and Sun are exactly on opposite sides of the Earth. | Visible from many parts of Earth where the Moon is above the horizon. | The Moon appears red because some sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere, filtering out blue light. |
| Partial Lunar Eclipse | Occurs when only a part of the Moon enters Earth’s shadow. | Only the partially shadowed Moon is visible. |
The shadowed part of the Moon looks very dark from Earth. |
| Penumbral Lunar Eclipse | The Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbral shadow (outer shadow). | Difficult to observe as the shadow is faint and subtle. |
The Moon looks slightly dim but there is no major change in colour. |
The Earth’s Shadow on the Moon:
- Umbra: The darkest part of the Earth’s shadow. When the Moon moves into the umbra, a total lunar eclipse occurs (if fully covered) or a partial eclipse (if partly covered).
- Penumbra: The lighter outer part of the Earth’s shadow. When the Moon passes through the penumbra, a penumbral lunar eclipse occurs, causing the Moon to appear slightly dim.
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [1]
Complete the following table.
| Details | Lunar Eclipse | Solar Eclipse |
| Phase of the moon | New moon day | |
| Sequence | Moon-EarthSun | |
| Type of eclipse | ||
| Maximum duration of total eclipse | 107 minutes |
