1. Aim: To verify the Law of Conservation of Mass using chemical reactions.
2. Requirements
- Apparatus: conical flask, test tube, balance, airtight rubber cork.
- Chemicals: Calcium oxide (CaO), water (H₂O), calcium chloride (CaCl₂), sodium sulphate (Na₂SO₄).
3. Procedure
I: Reaction Between Calcium Oxide and Water
- Take 56 g of calcium oxide in a conical flask.
- Add 18 g of water to the flask.
- Observe the reaction and measure the mass of the substance formed.
Observation: A vigorous reaction occurs, producing a substance. The total mass of the substance formed equals the combined mass of calcium oxide and water.
Conclusion: The experiment confirms that the mass remains constant during the reaction, validating the Law of Conservation of Mass.
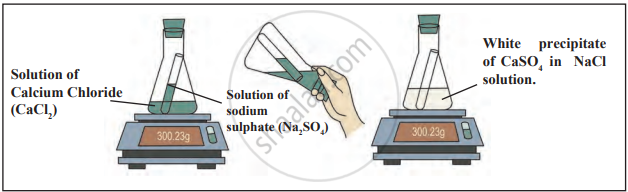
II: Reaction Between Calcium Chloride and Sodium Sulphate
- Add a solution of calcium chloride to a conical flask.
- Place a solution of sodium sulphate in a test tube and insert the test tube into the conical flask without mixing.
- Seal the flask with an airtight cork and weigh it using a balance.
- Tilt the flask to mix the solutions and allow the reaction to occur. Weigh the flask again after the reaction.
Observation: The reaction forms a white precipitate of calcium sulphate. The total mass of the flask and its contents remains unchanged before and after the reaction.
Conclusion: The mass remains constant during the reaction, confirming the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Verification of law of the chemical combination
