Topics
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Introduction of Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Nature of Chemistry
- Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Atomic and Molecular Masses
- Mole Concept
- Moles and Gases
Introduction to Analytical Chemistry
- Introduction of Analytical Chemistry
- Analysis
- Mathematical Operation and Error Analysis
- Determination of Molecular Formula
- Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometric Calculations
- Limiting Reagent
- Concentration of a Solution
- Use of Graph in Analysis
Basic Analytical Techniques
- Introduction of Some Analytical Techniques
- Purification of Solids
- Crystallisation Method
- Fractional Crystallization
- Simple Distillation Method
- Solvent Extraction
- Chromatography Method
- Adsorption Chromatography
- Partition Chromatography
Structure of Atom
- Subatomic Particles
- Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number
- Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones
- Drawbacks of Rutherford Atomic Model
- Bohr’s Atomic Model
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Chemical Bonding
- Introduction of Chemical Bonding
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Octet Rule
- Kossel and Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Formal Charge
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Limitations of the Octet Rule
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Valence Bond Theory
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Parameters of Covalent Bond
- Dipole Moment
- Resonance
Redox Reactions
- Introduction of Redox Reactions
- Oxidation Number
- Balancing Redox Reactions in Terms of Loss and Gain of Electrons
- Redox Reaction and Electrode Potential
Modern Periodic Table
- Introduction of Periodic Table
- Structure of the Modern Periodic Table
- Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration
- Blockwise Characteristics of Elements
- Periodic Trends in Elemental Properties
Elements of Group 1 and 2
- Hydrogen
- Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals
- Some Important Compounds of Elements of S-block
Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15
- Electronic Configuration of Elements of Groups 13, 14 and 15
- Trends in Atomic and Physical Properties of Elements of Groups 13, 14 and 15
- Chemical Properties of the Elements of the Groups 13,14 and 15
- Catenation
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Molecular Structures of Some Important Compounds of the Group 13, 14 and 15 Elements
- Chemistry of Notable Compounds of Elements of Groups 13, 14 and 15
States of Matter
- Introduction of States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid States
- Intermolecular Forces
- Characteristic Properties of Gases
- The Gas Laws
- Ideal Gas Equation
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Deviation from Ideal Behaviour
- Liquefaction of Gases and Critical Constant
- Liquid State
Adsorption and Colloids
- Introduction of Adsorption
- Adsorption
- Types of Adsorption
- Factors Affecting Adsorption of Gases on Solids
- Adsorption Isotherms (Freundlich and Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm)
- Applications of Adsorption
- Catalysis
- Adsorption Theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Colloids
Chemical Equilibrium
- Introduction of Chemical Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in Physical Processes
- Equilibrium in Chemical Processes - Dynamic Equilibrium
- Law of Mass Action and Equilibrium Constant
- Homogeneous and Heterogenous Equilibria
- Characteristics of Equilibrium Constant
- Applications of Equilibrium Constants
- Le Chaterlier's Principle and Factors Altering the Composition of Equilibrium
- Industrial Application
Nuclear Chemistry and Radioactivity
- Introduction: Nuclear Chemistry is a Branch of Physical Chemistry
- Classification of Nuclides
- Nuclear Stability
- Radioactivity
- Radioactive Decays
- Modes of Decay
- Nuclear Reactions
- Applications of Radio Isotopes
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Introduction of Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Structural Representation of Organic Molecules
- Classification of Organic Compounds
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Isomerism
- Theoretical Basis of Organic Reactions
Hydrocarbons
- Alkanes
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Basics of Food Chemistry
- Compounds with Medicinal Properties
- Cleansing Agents
- Introduction
- Experiment
Introduction:
Chromatography is a method used to separate different substances present in a small amount within the same solution. It helps identify and isolate the individual components of a mixture. This technique is widely used in pharmaceuticals, factories, and scientific research to detect new ingredients or study the composition of mixtures. For example, chromatography can be used to separate different colours from ink or identify chemicals in medicines.
Experiment
1. Aim: To separate different colours from the ink with the help of chromatography.
2. Requirements: filter paper, ink, jar, water, pencils, and scales.
3. Principle: An ink dye consists of several colours. These different dyes have different solubility. Dye with higher solubility in water dissolves quickly and moves fast with the water, and low solubility will move slowly, separating from each other.
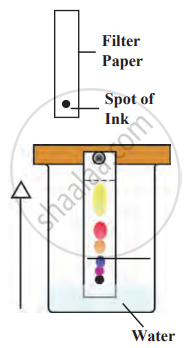
Chromatography
4. Procedure
- Take a thin strip of filter paper
- Draw a line on it using a pencil approximately 3 cm above the lower edge. Put a small drop of ink at the centre of the line. Let it dry.
- Lower the filter paper into a jar containing water so that the drop of ink on the paper is just above the water level, and leave it undisturbed. Cover the beaker with a lid to avoid evaporation.
- After some time, observe the ink as it moves up with the water.
5. Observation
- As water rises on the filter paper, the more soluble colours travel to the top, while the less soluble colours move upward at a slower rate.
- We get different colors on filter paper by chromatography
- In the process of chromatography, the coloured spot rises on the paper strip as it is soluble in water, and thus, due to its solubility, the spot rises up.
6. Inference/Result: The components of a mixture have varying solubility and can be separated using chromatography.
