Topics
Number Systems
Real Numbers
Algebra
Polynomials
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Introduction to linear equations in two variables
- Graphical Method
- Substitution Method
- Elimination Method
- Cross - Multiplication Method
- Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Consistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Inconsistency of Pair of Linear Equations
- Algebraic Conditions for Number of Solutions
- Simple Situational Problems
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Relation Between Co-efficient
Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Factorization
- Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
- Nature of Roots of a Quadratic Equation
- Relationship Between Discriminant and Nature of Roots
- Situational Problems Based on Quadratic Equations Related to Day to Day Activities to Be Incorporated
- Application of Quadratic Equation
Arithmetic Progressions
Coordinate Geometry
Lines (In Two-dimensions)
Constructions
- Division of a Line Segment
- Construction of Tangents to a Circle
- Constructions Examples and Solutions
Geometry
Triangles
- Similar Figures
- Similarity of Triangles
- Basic Proportionality Theorem (Thales Theorem)
- Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
- Areas of Similar Triangles
- Right-angled Triangles and Pythagoras Property
- Similarity of Triangles
- Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Acute Angle and Obtuse Angle
- Triangles Examples and Solutions
- Concept of Angle Bisector
- Similarity of Triangles
- Ratio of Sides of Triangle
Circles
Trigonometry
Introduction to Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric Ratios and Its Reciprocal
- Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles
- Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
- Trigonometric Identities
- Proof of Existence
- Relationships Between the Ratios
Trigonometric Identities
Some Applications of Trigonometry
Mensuration
Areas Related to Circles
- Perimeter and Area of a Circle - A Review
- Areas of Sector and Segment of a Circle
- Areas of Combinations of Plane Figures
- Circumference of a Circle
- Area of Circle
Surface Areas and Volumes
- Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
- Volume of a Combination of Solids
- Conversion of Solid from One Shape to Another
- Frustum of a Cone
- Concept of Surface Area, Volume, and Capacity
- Surface Area and Volume of Different Combination of Solid Figures
- Surface Area and Volume of Three Dimensional Figures
Statistics and Probability
Statistics
Probability
Internal Assessment
Definition
Whenever a point divides a line segment into two, three, four or any number of sections in a particular ratio then the formula used there is know as Section Formula.
Notes
1) Section Formula-Section Formula is derived as follows,
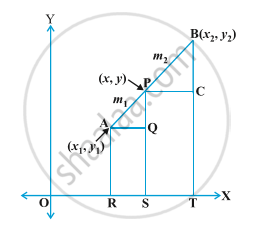
Let P be a point (x,y) which divides a line segment AB in the ratio `m_1:m_2`
`"AP"/"PB"= m_1/m_2`
Draw AR, PS and BT ⊥ OT
Also, draw AQ ⊥ PS, PC ⊥ BX
AQ=RS (Since AQSR forms a rectangle opposite sides are equal)
RS= OS-OR
Now, after watching carefully, we can see that OS have travelled `x` units and OR have travelled `x_1` units.
RS= (`x-x_1`)
Therefore, AQ= (`x-x_1`)
Similarly, PC=ST= (`x_2-x`)
and QP= PS-QS= (`y-y_1`)
also, BC= BT-CT= (`y_2-y`)
Clearly, ΔAQP and ΔPCB are similar triangle.
Therefore, `"AP"/"PB"= "AQ"/"PC"= "QP"/"CB"`
`m_1/m_2= (x-x_1)/(x_2-x) =( y-y_1)/(y_2-y)`
`m_1/m_2= (x-x_1)/(x_2-x)` and `m_1/m_2= (y-y_1)/y_2-y`
`m_1x_2-m_1x = m_2x-m_2x_1` and `m_1y_2-m_1y = m_2y-m_2y_1`
`m_1x_2+m_2x_1= m_1x+m_2x ` and `m_1y_2+m_2y_1= m_1y+m_2y`
`m_1x_2+m_2x_1= x(m_1+m_2)` and `m_1y_2+m_2y_1= y(m_1+m_2)`
x= `(m_1x_2+m_2x_1)/(m_1+m_2)` and `y= (m_1y_2+m_2y_1)/(m_1+m_2)`
`P(x,y)= [(m_1x_2+m_2x_1)/(m_1+m_2), (m_1y_2+m_2y_1)/(m_1+m_2)]`
2) Midpoint Formula-
Here let's say P is midpoint and divides AB in equal ratio i.e 1:1
Thus, AP:PB= `m_1:m_2= 1:1`
`P(x,y)= [(1x_2+1x_1)/(1+1), (1y_2+1y_1)/(1+1)]`
`P(x,y)= [(x_2+x_1)/2, (y_2+y_1)/2]`
Therefore, midpoint formula= `[(x_2+x_1)/2, (y_2+y_1)/2]`
