Topics
Number Systems
Program Analysis
Introduction to C+ +
- Introduction to C++
- Character Sets
- Standard I/O Strems in C++
- Type Modifiers
- C++ Data Types
- Variables in C++
- Constants
- Compiler Tokens
- Operators in C++
- Comments in C++
- Scope and Visibility
- Control Statements
- Functions in C++
- Default Arguments
- Techniques used to pass Variables into C++ Functions
- Function Overloading
- Inline Functions
- Recursion
- Pointers in C++
- Arrays in C++
- References
- Type Conversion in Expressions
Visual Basic
- Introduction to Visual Basic
- One language Three Editions
- Study Of Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- Visual Basic Programming
- Few Common Methods
Introduction to Networking and Internet
- Introduction to Networking and Internet
- Networking Terms and Concepts
- Types of Networks
- Network Security
- Network Configurations
- Network Applications
- Variables
- Declaring variables
- Types of variables
- Operators
- Constants
- Arrays
- Functions
- Control Flow Statements
- Loop statements
- Nested Control Structures
- Event - driven Programming
Notes
Variables & its Declaration
Variables store value during program's execution. A variable has a name and value. The rules for variable name are:
- A variable name must begin with a letter.
- They must not exceed 255 characters.
- Two variables cannot have the same name.
- A variable name may include letters, numbers and underscore.
Use Dim following variable name to explicitly declare variables. Visual Basic creates undeclared variables implicitly, storing any value. If you want a specific datatype, add the suffix.
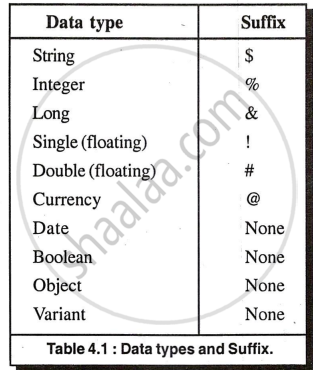
Constants & Arrays
Some variables do not change value during the execution of a program. These are constants. Constants are declared as: Const constantname [AS type] = value.
An array is a list of related items, like numbers, dates, or strings. Declare arrays with Dim, specifying the name and maximum elements.
For example, Dim Salary (15)
Control Flow Statements
Sometimes we need to check for a condition and take a different course of action on the test outcome. Visual Basic provides three control flow or decision structures:
- If – Then: The If -- Then structure tests the condition specified, and if it's true executes the statements (can be a single statement) that follow
- If -- Then – Else: This statement executes one block of statements if the condition is true and another if the condition is false.
- Select Case: The select case structure evaluates one expression and compares the result with multiple values. If a match is found, the corresponding statements are executed.
Loop Statements
i. DO --- LOOP: The DO -- LOOP executes a block of statements .for as Jong as the condition is true.
DO While condition
Stmtblock
LOOP or
DO Until condition
Stmtblock
LOOP
ii. For --- Next: The For -- Next loop requires that you know how many times the loop is executed. It uses a variable counter that increases or decreases in value during each repetition of the loop.
For counter= start to end [step increment]
statements
Next [counter]
iii.While --- Wend: The While - Wend loop executes a block of statements while the condition is true.
While condition
statements
Wend
If condition is True, all statements are executed, and when Wend is reached, control is returned to the while statement which evaluates condition again.
Exit statement
You may exit a For/Next loop using on Exit For statement. This will transfer program control to the statement following the Next statement.
