Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A charge Q is uniformly distributed on a spherical shell. What is the field at the centre of the shell? If a point charge is brought close to the shell, will the field at the centre change? Does your answer depend on whether the shell is conducting or non-conducting?
उत्तर
The field at the centre of the shell is zero. As all the charge given to a conductor resides on the surface, the field at any point inside the conducting sphere is zero. Also, the charge distribution at the surface is uniform; so all the electric field vectors due to these charges at the centre are equal and opposite. So, they cancel each other, resulting in a zero net value of the field.
When a charge is brought near the shell, due to induction, opposite polarity charges induce on the surface nearer to the charge and the same polarity charges appear on the face farther from the charge. In this way, a field is generated inside the shell. Hence, the field at the centre is non-zero.
Yes, our answer changes in case of a non-conducting spherical shell. As the charge given to the surface of a non-conducting spherical shell spreads non-uniformly, there is a net electric field at the centre of the sphere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use Gauss's law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
Find the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell at a point (i) outside the shell. Plot the graph of electric field with distance from the centre of the shell.
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R, which separates the two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 (n2 > n1). Draw the ray diagram and deduce the relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the radius of curvature (R) for refraction to take place at the convex spherical surface from rarer to denser medium.
A small conducting sphere of radius 'r' carrying a charge +q is surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius Ron which a charge +Q is placed. Using Gauss's law, derive the expressions for the electric field at a point 'x'
(i) between the sphere and the shell (r < x < R),
(ii) outside the spherical shell.
Using Gauss’ law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spherical conducting shell of radius R at a point
(i) outside and (ii) inside the shell.
Plot a graph showing variation of electric field as a function of r > R and r < R.
(r being the distance from the centre of the shell)
Using Gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
How is the field directed if (i) the sheet is positively charged, (ii) negatively charged?
A spherical shell made of plastic, contains a charge Q distributed uniformly over its surface. What is the electric field inside the shell? If the shell is hammered to deshape it, without altering the charge, will the field inside be changed? What happens if the shell is made of a metal?
A rubber balloon is given a charge Q distributed uniformly over its surface. Is the field inside the balloon zero everywhere if the balloon does not have a spherical surface?
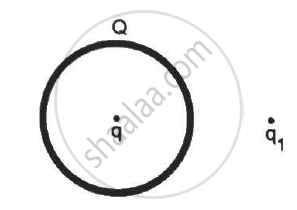
A thin, metallic spherical shell contains a charge Q on it. A point charge q is placed at the centre of the shell and another charge q1 is placed outside it as shown in the following figure . All the three charges are positive. The force on the charge at the centre is ____________.
A positive point charge Q is brought near an isolated metal cube.
Find the flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius R due to a charge of 10−7 C at the centre and another equal charge at a point 2R away from the centre in the following figure.
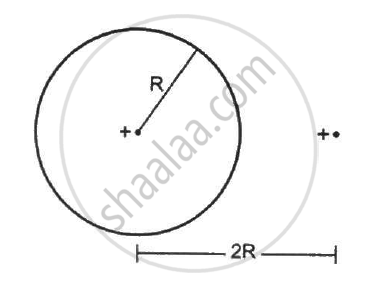
A spherical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density 2.0 × 10 -4 Cm-3 Find the electric field at a point inside the volume at a distance 4⋅0 cm from the centre.
A circular wire-loop of radius a carries a total charge Q distributed uniformly over its length. A small length dL of the wire is cut off. Find the electric field at the centre due to the remaining wire.
“A uniformly charged conducting spherical shell for the points outside the shell behaves as if the entire charge of the shell is concentrated at its centre”. Show this with the help of a proper diagram and verify this statement.
