Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
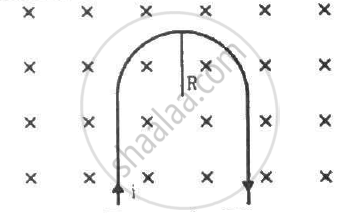
A rigid wire consists of a semi-circular portion of radius R and two straight sections (figure). The wire is partially immersed in a perpendicular magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. Find the magnetic force on the wire if it carries a current i.
उत्तर
Given:-
Radius of the semi-circular portion of the rigid wire = R
Magnetic field = B
Electric current flowing through the wire = i
As per the question, the wire is partially immersed in a perpendicular magnetic field.
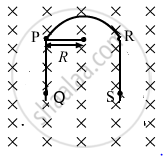
As PQ and RS are straight wires of length l each and strength of the magnetic field is also same on both the wires, the force acting on these wires will be equal in magnitude but their directions will be opposite to each other.(Direction of force can be found out using Fleming's left hand rule.)
So, the magnetic force on the wire PQ and the force on the wire RS are equal and opposite to each other. Both the forces cancel each other.
Therefore, only the semicircular loop PR will experience a net magnetic force.
Here, angle between the length of the wire and magnetic field, θ = 90˚
Magnetic force in the loop PR,
`vecF = iveclxxvecB`
Here, l = 2R
`vecF=i2R xx vecB`
`vecF = i2RB sin90^circ`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small compass needle of magnetic moment ‘m’ is free to turn about an axis perpendicular to the direction of uniform magnetic field ‘B’. The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is ‘I’. The needle is slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it executes simple harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time period.
A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 0.9 J/T is placed with its axis at 30° to a uniform magnetic field. It experiences a torque of 0.063 J.
(i) Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field.
(ii) In which orientation will the bar magnet be in stable equilibrium in the magnetic field?
Which of the following particles will have minimum frequency of revolution when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
A vertical wire carries a current in upward direction. An electron beam sent horizontally towards the wire will be deflected
Two parallel wires carry currents of 20 A and 40 A in opposite directions. Another wire carying a current anti parallel to 20 A is placed midway between the two wires. T he magnetic force on it will be
A wire of length l carries a current i long the x-axis. A magnetic field exists, which is given as `vecB = B_0 (veci + vecj + veck)` T. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the wire.
A current of 5.0 A exists in the circuit shown in the figure. The wire PQ has a length of 50 cm and the magnetic field in which it is immersed has a magnitude of 0.20 T. Find the magnetic force acting on the wire PQ.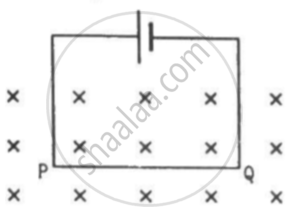
Consider a non-conducting plate of radius r and mass m that has a charge q distributed uniformly over it. The plate is rotated about its axis with an angular speed ω. Show that the magnetic moment µ and the angular momentum l of the plate are related as `mu = q/(2 m)l`
Consider a straight piece of length x of a wire carrying a current i. Let P be a point on the perpendicular bisector of the piece, situated at a distance d from its middle point. Show that for d >> x, the magnetic field at P varies as 1/d2 whereas for d << x, it varies as 1/d.
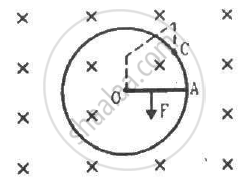
Consider the situation shown in the figure. Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. Find the magnitude of this force when the rod makes an angle θ with the vertical.
A straight horizontal conducting rod of length 0.45 m and mass 60 g is suspended by two vertical wires at its ends. A current of 5.0 A is set up in the rod through the wires.
(a) What magnetic field should be set up normal to the conductor in order that the tension in the wires is zero?
(b) What will be the total tension in the wires if the direction of current is reversed keeping the magnetic field same as before?
(Ignore the mass of the wires) g = 9.8 m s–2.
Correct expression for force on a current carrying conductor of length dl in a magnetic field is ______.
When a magnetic compass needle is carried nearby to a straight wire carrying current, then
- the straight wire cause a noticeable deflection in the compass needle.
- the alignment of the needle is tangential to an imaginary circle with straight wire as its centre and has a plane perpendicular to the wire.
A charged particle is moving on circular path with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B, if the velocity of the charged particle is doubled and strength of magnetic field is halved, then radius becomes ______.
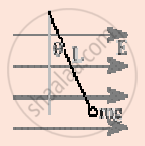
A small object with charge q and weight mg is attached to one end of a string of length ‘L’ attached to a stationary support. The system is placed in a uniform horizontal electric field ‘E’, as shown in the accompanying figure. In the presence of the field, the string makes a constant angle θ with the vertical. The sign and magnitude of q ______.
A current of 3 A is flowing in a linear conductor having a length of 40 cm. The conductor is placed in a magnetic field of strength of 500 gauss and makes an angle of 30° with the direction of the field. It experiences a force of magnitude:
A straight conductor of length 2m moves at a speed of 20 m/s. When the conductor makes an angle of 30° with the direction of magnetic field of induction of 0.1 wbm2 then induced emf:
A conducting loop of resistance R and radius r has its centre at the origin of the coordinate system in a magnetic field of induction B. When it is rotated about y-axis through 90°, the net charge flown in the loop is directly proportional to: