Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A straight horizontal wire of mass 10 mg and length 1.0 m carries a current of 2.0 A. What minimum magnetic field B should be applied in the region, so that the magnetic force on the wire may balance its weight?
उत्तर
Given:
Mass of the wire, M = 10 mg = 10−5 Kg
Length of the wire, l = 1.0 m
Electric current flowing through wire, I = 2.0 A
As per the question, the weight of the wire should be balanced by the magnetic force acting on the wire.Also angle between the length of the wire and magnetic field is 90°
Thus, Mg = IlB, where
g is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s2
B is the applied magnetic field
So,
`B = (Mg)/(Il)`
= `(10^-5xx9.8)/(2xx1)`
= 4.9 ×10-5 T
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
A horizontal overhead power line carries a current of 90 A in east to west direction. What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the current 1.5 m below the line?
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and original coil.
A charged particle is in motion having initial velocity `vecv` when it enters into a region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to `vecv`. Because of the magnetic force the kinetic energy of the particle will ______.
A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out of it following a complicated trajectory. Would its final speed equal the initial speed if it suffered no collisions with the environment?
A deuteron of kinetic energy 50 keV is describing a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The kinetic energy of the proton that describes a circular orbit of radius 0.5 metre in the same plane with the same B is ______.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
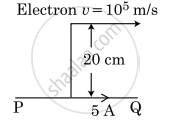
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein ______.
- E = 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B ≠ 0.
- E ≠ 0, B = 0.
- E = 0, B = 0.
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]–1.
A charge particle moves along circular path in a uniform magnetic field in a cyclotron. The kinetic energy of the charge particle increases to 4 times its initial value. What will be the ratio of new radius to the original radius of circular path of the charge particle:
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
State the expression for the Lorentz force on a charge due to an electric field as well as a magnetic field. Hence discuss the magnetic force on a charged particle which is (i) moving parallel to the magnetic field and (ii) stationary.
Two long parallel current-carrying conductors are 0.4 m apart in air and carry currents 5 A and 10 A. Calculate the force per metre on each conductor, if the currents are (a) in the same direction and (b) in the opposite direction.
Lorentz force in vector form is ______.
