Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A triangle ABC is right angled at A. L is a point on BC such that AL ⊥ BC. Prove that ∠BAL = ∠ACB.
उत्तर
Given In ΔABC, ∠A = 90° and AL ⊥ BC
To prove ∠BAL = ∠ACB
Proof In ΔABC and ΔLAC, ∠BAC = ∠ALC [Each 90°] ...(i)
And ∠ABC = ∠ABL [Common angle] ...(ii)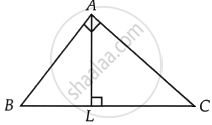
On adding equation (i) and (ii), we get
∠BAC + ∠ABC = ∠ALC + ∠ABL ...(iii)
Again, in ΔABC,
∠BAC + ∠ACB + ∠ABC = 180° ...[Sum of all angles of a triangle is 180°]
⇒ ∠BAC + ∠ABC = 180° – ∠ACB ...(iv)
In ΔABL,
∠ABL + ∠ALB + ∠BAL = 180° ...[Sum of all angles of a triangle is 180°]
⇒ ∠ABL + ∠ALC = 180° – ∠BAL ...[∴ ∠ALC = ∠ALB = 90°] ...(v)
On substituting the value from equations (iv) and (v) in equation (iii), we get
180° – ∠ACS = 180° – ∠SAL
⇒ ∠ACB = ∠BAL
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
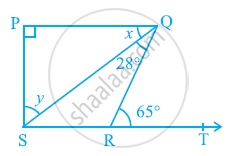
In the given figure, if PQ ⊥ PS, PQ || SR, ∠SQR = 28º and ∠QRT = 65º, then find the values of x and y.
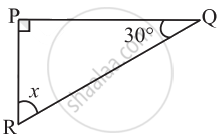
Find the value of the unknown x in the following diagram:
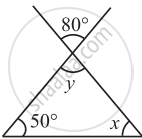
Find the value of the unknown x and y in the following diagram:
In the following triangle, find the value of x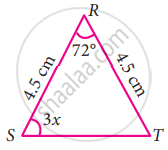
If the three angles of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 4, then find them
How many triangles can be drawn having its angles as 45°, 64° and 72°? Give reason for your answer.
In ∆PQR, if PQ = QR and ∠Q = 100°, then ∠R is equal to ______.
In the given figure, find the values of a, b and c
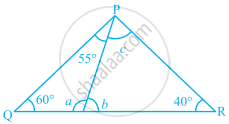
In the given figure, find the measures of ∠PON and ∠NPO.
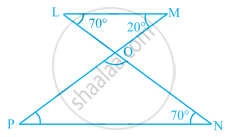
In a right-angled triangle if an angle measures 35°, then find the measure of the third angle.
