Advertisements
Chapters
2: Polynomials
3: Coordinate Geometry
4: Linear Equation In Two Variables
5: Introduction To Euclid's Geometry
▶ 6: Lines & Angles
7: Triangles
8: Quadrilaterals
9: Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles
10: Circles
11: Construction
12: Heron's Formula
13: Surface Area & Volumes
14: Statistics & Probability
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Lines & Angles NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Lines & Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Lines & Angles
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 9.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 6 Lines & Angles Exercise 6.1 [Pages 55 - 56]
Choose the correct alternative:
In the following figure, if AB || CD || EF, PQ || RS, ∠RQD = 25° and ∠CQP = 60°, then ∠QRS is equal to ______.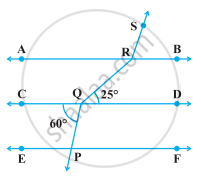
85°
135°
145°
110°
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is ______.
an isosceles triangle
an obtuse triangle
an equilateral triangle
a right triangle
An exterior angle of a triangle is 105° and its two interior opposite angles are equal. Each of these equal angles is ______.
`37 1^circ/2`
`52 1^circ/2`
`72 1^circ/2`
75°
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 5 : 3 : 7. The triangle is ______.
an acute angled triangle
an obtuse angled triangle
a right triangle
an isosceles triangle
If one of the angles of a triangle is 130°, then the angle between the bisectors of the other two angles can be ______.
50°
65°
145°
155°
In the following figure, POQ is a line. The value of x is ______.
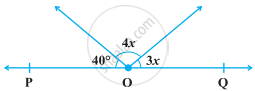
20°
25°
30°
35°
In the following figure, if OP || RS, ∠OPQ = 110° and ∠QRS = 130°, then ∠PQR is equal to ______.

40°
50°
60°
70°
Angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 3. The smallest angle of the triangle is ______.
60°
40°
80°
20°
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 6 Lines & Angles Exercise 6.2 [Pages 56 - 57]
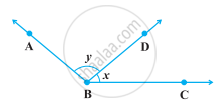
For what value of x + y in figure will ABC be a line? Justify your answer.
Can a triangle have all angles less than 60°? Give reason for your answer.
Can a triangle have two obtuse angles? Give reason for your answer.
How many triangles can be drawn having its angles as 45°, 64° and 72°? Give reason for your answer.
How many triangles can be drawn having its angles as 53°, 64° and 63°? Give reason for your answer.
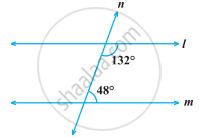
In the following figure, find the value of x for which the lines l and m are parallel.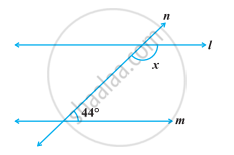
Two adjacent angles are equal. Is it necessary that each of these angles will be a right angle? Justify your answer.
If one of the angles formed by two intersecting lines is a right angle, what can you say about the other three angles? Give reason for your answer.
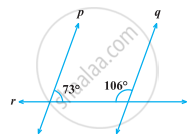
In the following figure, which of the two lines are parallel and why?
 |
 |
Two lines l and m are perpendicular to the same line n. Are l and m perpendicular to each other? Give reason for your answer.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 6 Lines & Angles Exercise 6.3 [Pages 58 - 60]
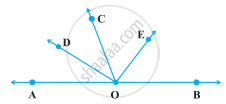
In the following figure, OD is the bisector of ∠AOC, OE is the bisector of ∠BOC and OD ⊥ OE. Show that the points A, O and B are collinear.
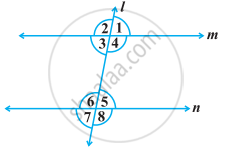
In the following figure, ∠1 = 60° and ∠6 = 120°. Show that the lines m and n are parallel.
AP and BQ are the bisectors of the two alternate interior angles formed by the intersection of a transversal t with parallel lines l and m (Figure). Show that AP || BQ.
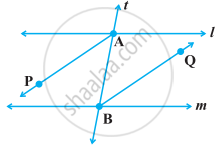
In the following figure, bisectors AP and BQ of the alternate interior angles are parallel, then show that l ||m.

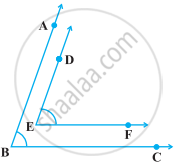
In the following figure, BA || ED and BC || EF. Show that ∠ABC = ∠DEF
[Hint: Produce DE to intersect BC at P (say)].
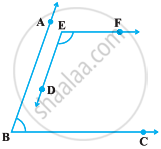
In the following figure, BA || ED and BC || EF. Show that ∠ABC + ∠DEF = 180°
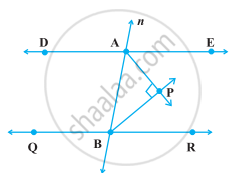
In the following figure, DE || QR and AP and BP are bisectors of ∠EAB and ∠RBA, respectively. Find ∠APB.
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. Find the angles of the triangle.
A triangle ABC is right angled at A. L is a point on BC such that AL ⊥ BC. Prove that ∠BAL = ∠ACB.
Two lines are respectively perpendicular to two parallel lines. Show that they are parallel to each other.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 6 Lines & Angles Exercise 6.4 [Pages 61 - 62]
If two lines intersect, prove that the vertically opposite angles are equal.
Bisectors of interior ∠B and exterior ∠ACD of a ∆ABC intersect at the point T. Prove that `∠BTC = 1/2 ∠BAC`.
A transversal intersects two parallel lines. Prove that the bisectors of any pair of corresponding angles so formed are parallel.
Prove that through a given point, we can draw only one perpendicular to a given line.
[Hint: Use proof by contradiction].
Prove that two lines that are respectively perpendicular to two intersecting lines intersect each other.
[Hint: Use proof by contradiction].
Prove that a triangle must have atleast two acute angles.
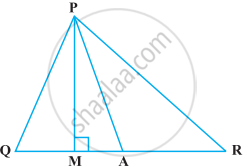
In the following figure, ∠Q > ∠R, PA is the bisector of ∠QPR and PM ⊥ QR. Prove that ∠APM = `1/2` (∠Q – ∠R).
Solutions for 6: Lines & Angles
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Lines & Angles NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Lines & Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Lines & Angles
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE 6 (Lines & Angles) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 6 Lines & Angles are Intersecting Lines and Non-intersecting Lines, Introduction to Lines and Angles, Basic Terms and Definitions, Introduction to Parallel Lines, Pairs of Angles, Parallel Lines and a Transversal, Angle Sum Property of a Triangle.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 9 solutions Lines & Angles exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Lines & Angles Mathematics [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
