Advertisements
Chapters
2: Polynomials
3: Coordinate Geometry
▶ 4: Linear Equation In Two Variables
5: Introduction To Euclid's Geometry
6: Lines & Angles
7: Triangles
8: Quadrilaterals
9: Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles
10: Circles
11: Construction
12: Heron's Formula
13: Surface Area & Volumes
14: Statistics & Probability
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 - Linear Equation In Two Variables NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 - Linear Equation In Two Variables - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Linear Equation In Two Variables
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 9.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 4 Linear Equation In Two Variables Exercise 4.1 [Pages 34 - 36]
Choose the correct alternative:
The linear equation 2x – 5y = 7 has ______.
A unique solution
Two solutions
Infinitely many solutions
No solution
The equation 2x + 5y = 7 has a unique solution, if x, y are ______.
Natural numbers
Positive real numbers
Real numbers
Rational numbers
If (2, 0) is a solution of the linear equation 2x + 3y = k, then the value of k is ______.
4
6
5
2
Any solution of the linear equation 2x + 0y + 9 = 0 in two variables is of the form ______.
`(- 9/2, m)`
`(n, - 9/2)`
`(0, - 9/2)`
(– 9, 0)
The graph of the linear equation 2x + 3y = 6 cuts the y-axis at the point ______.
(2, 0)
(0, 3)
(3, 0)
(0, 2)
The equation x = 7, in two variables, can be written as ______.
1 . x + 1 . y = 7
1 . x + 0 . y = 7
0 . x + 1 . y = 7
0 . x + 0 . y = 7
Any point on the x-axis is of the form ______.
(x, y)
(0, y)
(x, 0)
(x, x)
Any point on the line y = x is of the form ______.
(a, a)
(0, a)
(a, 0)
(a, – a)
The equation of x-axis is of the form ______.
x = 0
y = 0
x + y = 0
x = y
The graph of y = 6 is a line ______.
parallel to x-axis at a distance 6 units from the origin
parallel to y-axis at a distance 6 units from the origin
making an intercept 6 on the x-axis
making an intercept 6 on both the axes
x = 5, y = 2 is a solution of the linear equation ______.
x + 2y = 7
5x + 2y = 7
x + y = 7
5x + y = 7
If a linear equation has solutions (–2, 2), (0, 0) and (2, –2), then it is of the form ______.
y – x = 0
x + y = 0
–2x + y = 0
–x + 2y = 0
The positive solutions of the equation ax + by + c = 0 always lie in the ______.
1st quadrant
2nd quadrant
3rd quadrant
4th quadrant
The graph of the linear equation 2x + 3y = 6 is a line which meets the x-axis at the point ______.
(0, 2)
(2, 0)
(3, 0)
(0, 3)
The graph of the linear equation y = x passes through the point ______.
`(3/2, (-3)/2)`
`(0, 3/2)`
(1, 1)
`((-1)/2, 1/2)`
If we multiply or divide both sides of a linear equation with a non-zero number, then the solution of the linear equation ______.
Changes
Remains the same
Changes in case of multiplication only
Changes in case of division only
How many linear equations in x and y can be satisfied by x = 1 and y = 2?
Only one
Two
Infinitely many
Three
The point of the form (a, a) always lies ______.
x-axis
y-axis
On the line y = x
On the line x + y = 0
The point of the form (a, – a) always lies on the line ______.
x = a
y = – a
y = x
x + y = 0
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 4 Linear Equation In Two Variables Exercise 4.2 [Page 37]
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The point (0, 3) lies on the graph of the linear equation 3x + 4y = 12.
True
False
The graph of the linear equation x + 2y = 7 passes through the point (0, 7).
True
False
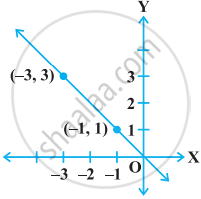
The graph given below represents the linear equation x + y = 0.
True
False
The graph given below represents the linear equation x = 3 (see figure).

True
False
The coordinates of points in the table:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| y | 2 | 3 | 4 | –5 | 6 |
represent some of the solutions of the equation x – y + 2 = 0.
True
False
Every point on the graph of a linear equation in two variables does not represent a solution of the linear equation.
True
False
The graph of every linear equation in two variables need not be a line.
True
False
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 4 Linear Equation In Two Variables Exercise 4.3 [Pages 38 - 39]
Draw the graphs of linear equations y = x and y = – x on the same cartesian plane. What do you observe?
Determine the point on the graph of the linear equation 2x + 5y = 19, whose ordinate is `1 1/2` times its abscissa.
Draw the graph of the equation represented by a straight line which is parallel to the x-axis and at a distance 3 units below it.
Draw the graph of the linear equation whose solutions are represented by the points having the sum of the coordinates as 10 units.
Write the linear equation such that each point on its graph has an ordinate 3 times its abscissa.
If the point (3, 4) lies on the graph of 3y = ax + 7, then find the value of a.
How many solution(s) of the equation 2x + 1 = x – 3 are there on the number line?
How many solution(s) of the equation 2x + 1 = x – 3 are there on the cartesian plane?
Find the solution of the linear equation x + 2y = 8 which represents a point on x-axis.
Find the solution of the linear equation x + 2y = 8 which represents a point on y-axis.
For what value of c, the linear equation 2x + cy = 8 has equal values of x and y for its solution.
Let y varies directly as x. If y = 12 when x = 4, then write a linear equation. What is the value of y when x = 5?
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 4 Linear Equation In Two Variables Exercise 4.4 [Pages 41 - 42]
Show that the points A(1, 2), B(– 1, – 16) and C(0, – 7) lie on the graph of the linear equation y = 9x – 7.
The following observed values of x and y are thought to satisfy a linear equation. Write the linear equation:
| x | 6 | – 6 |
| y | –2 | 6 |
Draw the graph using the values of x, y as given in the above table. At what points the graph of the linear equation
- cuts the x-axis
- cuts the y-axis
Draw the graph of the linear equation 3x + 4y = 6. At what points, the graph cuts the x-axis and the y-axis.
The linear equation that converts Fahrenheit (F) to Celsius (C) is given by the relation
`C = (5F - 160)/9`
- If the temperature is 86°F, what is the temperature in Celsius?
- If the temperature is 35°C, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit?
- If the temperature is 0°C what is the temperature in Fahrenheit and if the temperature is 0°F, what is the temperature in Celsius?
- What is the numerical value of the temperature which is same in both the scales?
If the temperature of a liquid can be measured in Kelvin units as x°K or in Fahrenheit units as y°F, the relation between the two systems of measurement of temperature is given by the linear equation
`y = 9/5 (x - 273) + 32`
- Find the temperature of the liquid in Fahrenheit if the temperature of the liquid is 313°K.
- If the temperature is 158°F, then find the temperature in Kelvin.
The force exerted to pull a cart is directly proportional to the acceleration produced in the body. Express the statement as a linear equation of two variables and draw the graph of the same by taking the constant mass equal to 6 kg. Read from the graph, the force required when the acceleration produced is (i) 5 m/sec2, (ii) 6 m/sec2.
Solutions for 4: Linear Equation In Two Variables
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 - Linear Equation In Two Variables NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 - Linear Equation In Two Variables - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 - Linear Equation In Two Variables
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE 4 (Linear Equation In Two Variables) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 4 Linear Equation In Two Variables are Solution of a Linear Equation, Graph of a Linear Equation in Two Variables, Equations of Lines Parallel to the X-axis and Y-axis, Introduction to linear equations in two variables, Linear Equation in One Variable.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 9 solutions Linear Equation In Two Variables exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Linear Equation In Two Variables Mathematics [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
