Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An aeroplane has to go from a point A to another point B, 500 km away due 30° east of north. A wind is blowing due north at a speed of 20 m/s. The air-speed of the plane is 150 m/s. Find the time taken by the plane to go from A to B.
उत्तर
Given:
Distance between points A and B = 500 km
B from A is 30˚ east of north.
Speed of wind due north, vw = 20 m/s
Airspeed of the plane, va = 150 m/s
Let \[\vec{R}\] be the resultant direction of the plane to reach point B.
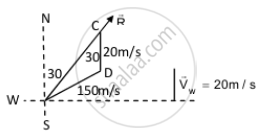
Time taken by the plane to reach point B from point A: \[\sin^{- 1} \left( \frac{1}{15} \right) = 3^\circ 48'\]
⇒ 30° + 3°48' = 33°48
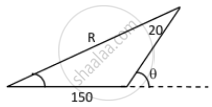
\[R = \sqrt{A^2 + B^2 + 2AB\cos\theta}\]
\[R = \sqrt{150 + 20 + 2\left( 150 \right)\left( 20 \right) \cos\left( 33^\circ48' \right)}\]
\[ = \sqrt{27886} = 167 \text{ m/s } \]
\[\text{ Time } = \frac{s}{v} = \frac{500000}{167}\]
\[ = 2994 s = 49 . 0 \approx 50 \text{ minutes } \]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 m s–1.
- What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball?
- What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion?
- Choose the x = 0 m and t = 0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically downward direction to be the positive direction of x-axis, and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion.
- To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hands? (Take g = 9.8 m s–2 and neglect air resistance).
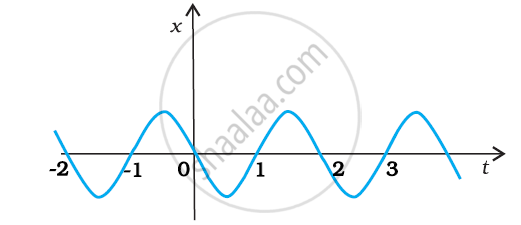
The following figure gives the x-t plot of a particle executing one-dimensional simple harmonic motion. Give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration variables of the particle at t = 0.3 s, 1.2 s, – 1.2 s.
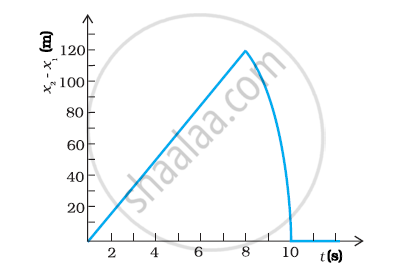
Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff 200 m high with initial speeds of 15 m/s and 30 m/s. Verify that the graph shown in Fig. 3.27 correctly represents the time variation of the relative position of the second stone with respect to the first. Neglect air resistance and assume that the stones do not rebound after hitting the ground. Take g = 10 m/s2. Give the equations for the linear and curved parts of the plot.
The velocity of a particle is towards west at an instant. Its acceleration is not towards west, not towards east, not towards north and towards south. Give an example of this type of motion .
In a projectile motion the velocity
Two bullets are fired simultaneously, horizontally and with different speeds from the same place. Which bullet will hit he ground first?
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the maximum speed attained by the train .
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the average velocity during this period .
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the distance travelled by the particle during this period.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 28 m/s. change if the initial speed is more than 28 m/s such as 40 m/s or 80 m/s ?
An elevator is descending with uniform acceleration. To measure the acceleration, a person in the elevator drops a coin at the moment the elevator starts. The coin is 6 ft above the floor of the elevator at the time it is dropped. The person observes that the coin strikes the floor in 1 second. Calculate from these data the acceleration of the elevator.
A ball is thrown horizontally from a point 100 m above the ground with a speed of 20 m/s. Find the horizontal distance it travels before reaching the ground .
A ball is thrown horizontally from a point 100 m above the ground with a speed of 20 m/s. Find the velocity (direction and magnitude) with which it strikes the ground.
A popular game in Indian villages is goli which is played with small glass balls called golis. The goli of one player is situated at a distance of 2.0 m from the goli of the second player. This second player has to project his goli by keeping the thumb of the left hand at the place of his goli, holding the goli between his two middle fingers and making the throw. If the projected goli hits the goli of the first player, the second player wins. If the height from which the goli is projected is 19.6 cm from the ground and the goli is to be projected horizontally, with what speed should it be projected so that it directly hits the stationery goli without falling on the ground earlier?
A person standing on the top of a cliff 171 ft high has to throw a packet to his friend standing on the ground 228 ft horizontally away. If he throws the packet directly aiming at the friend with a speed of 15.0 ft/s, how short will the packet fall?
Find the average velocity of a projectile between the instants it crosses half the maximum height. It is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal.
A bomb is dropped from a plane flying horizontally with uniform speed. Show that the bomb will explode vertically below the plane. Is the statement true if the plane flies with uniform speed but not horizontally?
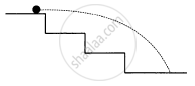
A staircase contains three steps each 10 cm high and 20 cm wide (in the following figure). What should be the minimum horizontal velocity of a ball rolling of the uppermost plane so as to hit directly the lowest plane ?
A person is standing on a truck moving with a constant velocity of 14.7 m/s on a horizontal road. The man throws a ball in such a way that it returns to the truck after the truck has moved 58.8 m. Find the speed and the angle of projection as seen from the road.
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. If he heads in a direction making an angle θ with the flow, find the time he takes to cross the river.
