Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on another. This is because ______.
विकल्प
the two magnetic forces are equal and opposite, so they produce no net effect.
the magnetic forces do no work on each particle.
the magnetic forces do equal and opposite (but non-zero) work on each particle.
the magenetic forces are necessarily negligible.
उत्तर
An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on another. This is because the magnetic forces do no work on each particle.
Explanation:
The work-energy theorem states that net work done equals final kinetic energy - the initial kinetic energy of the item.
The following equation demonstrates the relationship between work and kinetic energy:
∑W = K2 – K1v
As the electron and proton move under the influence of mutual interactions, the magnetic forces will be perpendicular to their motion, acting as a centripetal force for the particle.
As a result of performing the uniform circular motion in this manner, the particle's speed remains constant.
As a result, the particle's kinetic energy remains unchanged.
As a result, these forces perform no work.
`vecF_m = q(vecv xx vecB) * F_m` (magnetic force) will be perpendicular to both B and v, where B represents the external magnetic field and v represents particle velocity.
That is why the magnetic pull of one particle on another is ignored.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
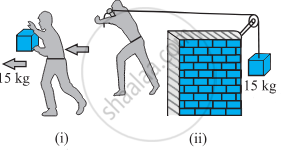
In Figure (i) the man walks 2 m carrying a mass of 15 kg on his hands. In Figure (ii), he walks the same distance pulling the rope behind him. The rope goes over a pulley, and a mass of 15 kg hangs at its other end. In which case is the work done greater?
In a factory, 2000 kg of metal needs to be lifted by an engine through a distance of 12 m in 1 minute. Find the minimum horsepower of the engine to be used.
A small block of mass 200 g is kept at the top of a frictionless incline which is 10 m long and 3⋅2 m high. How much work was required (a) to lift the block from the ground and put it an the top, (b) to slide the block up the incline? What will be the speed of the block when it reaches the ground if (c) it falls off the incline and drops vertically to the ground (d) it slides down the incline? Take g = 10 m/s2.
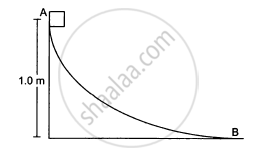
A block weighing 10 N travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to a rough horizontal surface (In the following figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of 0⋅20 with the block. If the block starts slipping on the track from a point 1⋅0 m above the horizontal surface, how far will it move on the rough surface?
A block of mass 5 kg is suspended from the end of a vertical spring which is stretched by 10 cm under the load of the block. The block is given a sharp impulse from below, so that it acquires an upward speed of 2 m/s. How high will it rise? Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting from the topmost point. Find the angle rotated by the radius through the particle, when it leaves contact with the sphere.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Suppose the chain is released and slides down the sphere. Find the kinetic energy of the chain, when it has slid through an angle θ.
Two bodies of unequal mass are moving in the same direction with equal kinetic energy. The two bodies are brought to rest by applying retarding force of same magnitude. How would the distance moved by them before coming to rest compare?
A rocket accelerates straight up by ejecting gas downwards. In a small time interval ∆t, it ejects a gas of mass ∆m at a relative speed u. Calculate KE of the entire system at t + ∆t and t and show that the device that ejects gas does work = `(1/2)∆m u^2` in this time interval (neglect gravity).
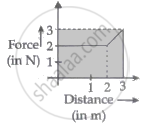
A particle moves in one dimension from rest under the influence of a force that varies with the distance travelled by the particle as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the particle after it has travelled 3 m is ______.