Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
As one considers orbits with higher values of n in a hydrogen atom, the electric potential energy of the atom
विकल्प
decreases
increases
remains the same
does not increase
उत्तर
increases
The electric potential energy of hydrogen atom with electron at the nth state is given by
V = - `(2xx13.6)/n^2`
As the value of n increases, the potential energy of the hydrogen atom also increases, i.e. the atom becomes less bound as n increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. What series of wavelengths will be emitted?
Classically, an electron can be in any orbit around the nucleus of an atom. Then what determines the typical atomic size? Why is an atom not, say, a thousand times bigger than its typical size? The question had greatly puzzled Bohr before he arrived at his famous model of the atom that you have learnt in the text. To simulate what he might well have done before his discovery, let us play as follows with the basic constants of nature and see if we can get a quantity with the dimensions of length that is roughly equal to the known size of an atom (~ 10−10 m).
(a) Construct a quantity with the dimensions of length from the fundamental constants e, me, and c. Determine its numerical value.
(b) You will find that the length obtained in (a) is many orders of magnitude smaller than the atomic dimensions. Further, it involves c. But energies of atoms are mostly in non-relativistic domain where c is not expected to play any role. This is what may have suggested Bohr to discard c and look for ‘something else’ to get the right atomic size. Now, the Planck’s constant h had already made its appearance elsewhere. Bohr’s great insight lay in recognising that h, me, and e will yield the right atomic size. Construct a quantity with the dimension of length from h, me, and e and confirm that its numerical value has indeed the correct order of magnitude.
When white radiation is passed through a sample of hydrogen gas at room temperature, absorption lines are observed in Lyman series only. Explain.
What will be the energy corresponding to the first excited state of a hydrogen atom if the potential energy of the atom is taken to be 10 eV when the electron is widely separated from the proton? Can we still write En = E1/n2, or rn = a0 n2?
In which of the following systems will the radius of the first orbit (n = 1) be minimum?
Which of the following curves may represent the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom as a function of trincipal quantum number n?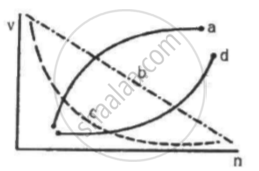
Which of the following products in a hydrogen atom are independent of the principal quantum number n? The symbols have their usual meanings.
(a) vn
(b) Er
(c) En
(d) vr
Calculate the smallest wavelength of radiation that may be emitted by (a) hydrogen, (b) He+ and (c) Li++.
Find the binding energy of a hydrogen atom in the state n = 2.
(a) Find the first excitation potential of He+ ion. (b) Find the ionization potential of Li++ion.
A group of hydrogen atoms are prepared in n = 4 states. List the wavelength that are emitted as the atoms make transitions and return to n = 2 states.
A hydrogen atom in a state having a binding energy of 0.85 eV makes transition to a state with excitation energy 10.2 e.V (a) Identify the quantum numbers n of the upper and the lower energy states involved in the transition. (b) Find the wavelength of the emitted radiation.
What is the energy of a hydrogen atom in the first excited state if the potential energy is taken to be zero in the ground state?
Suppose, in certain conditions only those transitions are allowed to hydrogen atoms in which the principal quantum number n changes by 2. (a) Find the smallest wavelength emitted by hydrogen. (b) List the wavelength emitted by hydrogen in the visible range (380 nm to 780 nm).
Electrons are emitted from an electron gun at almost zero velocity and are accelerated by an electric field E through a distance of 1.0 m. The electrons are now scattered by an atomic hydrogen sample in ground state. What should be the minimum value of E so that red light of wavelength 656.3 nm may be emitted by the hydrogen?
A hydrogen atom moving at speed υ collides with another hydrogen atom kept at rest. Find the minimum value of υ for which one of the atoms may get ionized.
The mass of a hydrogen atom = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
Positronium is just like a H-atom with the proton replaced by the positively charged anti-particle of the electron (called the positron which is as massive as the electron). What would be the ground state energy of positronium?
