Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following curves may represent the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom as a function of trincipal quantum number n?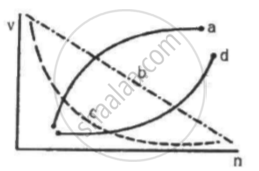
उत्तर
(c)
The speed (v) of electron can be expressed as
`v = (Ze^2)/(2∈_0hn)` ....(1)
Here,
Z = Number of protons in the nucleus
e = Magnitude of charge on electron charge
n = Principal quantum number
h = Planck's constant
It can be observed from equation (1) that the velocity of electron is inversely proportional to the principal quantum number (n).
Therefore, the graph between them must be a rectangular hyperbola.
The correct curve is (c).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. What series of wavelengths will be emitted?
If Bohr’s quantisation postulate (angular momentum = nh/2π) is a basic law of nature, it should be equally valid for the case of planetary motion also. Why then do we never speak of quantisation of orbits of planets around the sun?
The first excited energy of a He+ ion is the same as the ground state energy of hydrogen. Is it always true that one of the energies of any hydrogen-like ion will be the same as the ground state energy of a hydrogen atom?
Which wavelengths will be emitted by a sample of atomic hydrogen gas (in ground state) if electrons of energy 12.2 eV collide with the atoms of the gas?
In which of the following systems will the radius of the first orbit (n = 1) be minimum?
As one considers orbits with higher values of n in a hydrogen atom, the electric potential energy of the atom
The radius of the shortest orbit in a one-electron system is 18 pm. It may be
A hydrogen atom in ground state absorbs 10.2 eV of energy. The orbital angular momentum of the electron is increased by
Find the maximum Coulomb force that can act on the electron due to the nucleus in a hydrogen atom.
What is the energy of a hydrogen atom in the first excited state if the potential energy is taken to be zero in the ground state?
A gas of hydrogen-like ions is prepared in a particular excited state A. It emits photons having wavelength equal to the wavelength of the first line of the Lyman series together with photons of five other wavelengths. Identify the gas and find the principal quantum number of the state A.
Suppose, in certain conditions only those transitions are allowed to hydrogen atoms in which the principal quantum number n changes by 2. (a) Find the smallest wavelength emitted by hydrogen. (b) List the wavelength emitted by hydrogen in the visible range (380 nm to 780 nm).
The average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas at temperature T is 1.5 kT. Find the temperature at which the average kinetic energy of the molecules of hydrogen equals the binding energy of its atoms. Will hydrogen remain in molecular from at this temperature? Take k = 8.62 × 10−5 eV K−1.
Show that the ratio of the magnetic dipole moment to the angular momentum (l = mvr) is a universal constant for hydrogen-like atoms and ions. Find its value.
Electrons are emitted from an electron gun at almost zero velocity and are accelerated by an electric field E through a distance of 1.0 m. The electrons are now scattered by an atomic hydrogen sample in ground state. What should be the minimum value of E so that red light of wavelength 656.3 nm may be emitted by the hydrogen?
In a hydrogen atom the electron moves in an orbit of radius 0.5 A° making 10 revolutions per second, the magnetic moment associated with the orbital motion of the electron will be ______.
In the Auger process an atom makes a transition to a lower state without emitting a photon. The excess energy is transferred to an outer electron which may be ejected by the atom. (This is called an Auger electron). Assuming the nucleus to be massive, calculate the kinetic energy of an n = 4 Auger electron emitted by Chromium by absorbing the energy from a n = 2 to n = 1 transition.
