Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the following table:
| Car Model | Driver X Reaction time 0.20 s |
Driver Y Reaction time 0.30 s |
| A (deceleration on hard braking = 6.0 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Braking distance a = ............ Total stopping distance b = ............ |
Speed = 72 km/h Braking distance c = ........... Total stopping distance d = ............ |
| B (deceleration on hard braking = 7.5 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Breaking distance e = ........... Total stopping distance f = ............ |
Speed 72 km/h Braking distance g = ............. Total stopping distance h = ............ |
उत्तर
Braking distance: Distance travelled after the brakes are applied.
Total stopping distance = Braking distance + Distance travelled in the reaction time
Case A:
Deceleration = 6.0 m/s2
For driver X:
Initial velocity, u = 54 km/h = 15 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0
Braking distance,
Distance travelled in the reaction time = 15 × 0.20 = 3 m
Total stopping distance, b = 19 + 3 = 22 m
For driver Y:
Initial velocity, u = 72 km/h = 20 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0
Braking distance,
Total stopping distance, d = 33 + 6 = 39 m
Case B:
Deceleration = 6.0 m/s2
Now, we have:
e = 15 m
f = 18 m
g = 27 m
h = 33 m
| Car Model | Driver X Reaction Time = 0.20 s |
Driver Y Reaction Time = 0.30 s |
| A (deceleration on hard braking = 6.0 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Braking distance, a = 19 m Total stopping distance, b = 22 m |
Speed = 72 km/h Braking distance, c = 33 m Total stopping distance, d = 39 m |
| B (deceleration on hard braking = 7.5 m/s2) | Speed = 54 km/h Breaking distance, e = 15 m Total stopping distance, f = 18 m |
Speed = 72 km/h Braking distance, g = 27 m Total stopping distance, h = 33 m |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A car moving along a straight highway with a speed of 126 km h–1 is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. What is the retardation of the car (assumed uniform), and how long does it take for the car to stop?
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 m s–1.
- What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball?
- What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion?
- Choose the x = 0 m and t = 0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically downward direction to be the positive direction of x-axis, and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion.
- To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hands? (Take g = 9.8 m s–2 and neglect air resistance).
A ball is dropped from a height of 90 m on a floor. At each collision with the floor, the ball loses one tenth of its speed. Plot the speed-time graph of its motion between t = 0 to 12 s.
A three-wheeler starts from rest, accelerates uniformly with 1 m s–2 on a straight road for 10 s, and then moves with uniform velocity. Plot the distance covered by the vehicle during the nth second (n = 1,2,3….) versus n. What do you expect this plot to be during accelerated motion: a straight line or a parabola?
A boy standing on a stationary lift (open from above) throws a ball upwards with the maximum initial speed he can, equal to 49 m/s. How much time does the ball take to return to his hands? If the lift starts moving up with a uniform speed of 5 m/s and the boy again throws the ball up with the maximum speed he can, how long does the ball take to return to his hands?
At which point on its path a projectile has the smallest speed?
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the total distance moved by the train .
A bullet travelling with a velocity of 16 m/s penetrates a tree trunk and comes to rest in 0.4 m. Find the time taken during the retardation.
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the average velocity during this period .
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the time to reach the maximum height .
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the speed at half the maximum height. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A person sitting on the top of a tall building is dropping balls at regular intervals of one second. Find the positions of the 3rd, 4th and 5th ball when the 6th ball is being dropped.
A ball is dropped from a height of 5 m onto a sandy floor and penetrates the sand up to 10 cm before coming to rest. Find the retardation of the ball is sand assuming it to be uniform.
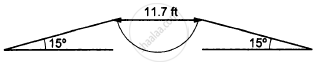
In the following figure shows a 11.7 ft wide ditch with the approach roads at an angle of 15° with the horizontal. With what minimum speed should a motorbike be moving on the road so that it safely crosses the ditch?
Assume that the length of the bike is 5 ft, and it leaves the road when the front part runs out of the approach road.
A person standing on the top of a cliff 171 ft high has to throw a packet to his friend standing on the ground 228 ft horizontally away. If he throws the packet directly aiming at the friend with a speed of 15.0 ft/s, how short will the packet fall?
A boy standing on a long railroad car throws a ball straight upwards. The car is moving on the horizontal road with an acceleration of 1 m/s2 and the projection velocity in the vertical direction is 9.8 m/s. How far behind the boy will the ball fall on the car?
A river 400 m wide is flowing at a rate of 2.0 m/s. A boat is sailing at a velocity of 10 m/s with respect to the water, in a direction perpendicular to the river. Find the time taken by the boat to reach the opposite bank.
Two friends A and B are standing a distance x apart in an open field and wind is blowing from A to B. A beat a drum and B hears the sound t1 time after he sees the event. A and B interchange their positions and the experiment is repeated. This time B hears the drum timer after he sees the event. Calculate the velocity of sound in still air v and the velocity of wind u. Neglect the time light takes in travelling between the friends.
