Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following terms :
Limiting molar conductivity
उत्तर
When concentration of an electrolyte approaches zero, then its molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.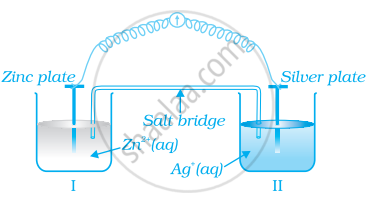
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
The limiting molar conductivities for Nacl, KBr and KCI are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. The limiting molar conductivity for Na Br is:-
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
The resistance of a conductivity cell with a 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 ohm. When the same cell is filled with a 0.02 M NaCl solution, the resistance is 1100 ohm. If the conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1, calculate the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl solution.
