Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define phase of S.H.M.
उत्तर
The physical quantity which describes the state of oscillation of a particle performing S.H.M at any instant is called phase of S.H.M.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the differential equation of linear simple harmonic motion.
A particle executes simple harmonic motion. If you are told that its velocity at this instant is zero, can you say what is its displacement? If you are told that its velocity at this instant is maximum, can you say what is its displacement?
A particle executes simple harmonic motion Let P be a point near the mean position and Q be a point near an extreme. The speed of the particle at P is larger than the speed at Q. Still the particle crosses Pand Q equal number of times in a given time interval. Does it make you unhappy?
In measuring time period of a pendulum, it is advised to measure the time between consecutive passage through the mean position in the same direction. This is said to result in better accuracy than measuring time between consecutive passage through an extreme position. Explain.
It is proposed to move a particle in simple harmonic motion on a rough horizontal surface by applying an external force along the line of motion. Sketch the graph of the applied force against the position of the particle. Note that the applied force has two values for a given position depending on whether the particle is moving in positive or negative direction.
A pendulum clock gives correct time at the equator. Will it gain time or loose time as it is taken to the poles?
A hollow sphere filled with water is used as the bob of a pendulum. Assume that the equation for simple pendulum is valid with the distance between the point of suspension and centre of mass of the bob acting as the effective length of the pendulum. If water slowly leaks out of the bob, how will the time period vary?
A platoon of soldiers marches on a road in steps according to the sound of a marching band. The band is stopped and the soldiers are ordered to break the steps while crossing a bridge. Why?
The motion of a particle is given by x = A sin ωt + B cos ωt. The motion of the particle is
A pendulum clock that keeps correct time on the earth is taken to the moon. It will run
A pendulum clock keeping correct time is taken to high altitudes,
Which of the following quantities are always negative in a simple harmonic motion?
(a) \[\vec{F} . \vec{a} .\]
(b) \[\vec{v} . \vec{r} .\]
(c) \[\vec{a} . \vec{r} .\]
(d)\[\vec{F} . \vec{r} .\]
Which of the following quantities are always positive in a simple harmonic motion?
A particle moves in the X-Y plane according to the equation \[\overrightarrow{r} = \left( \overrightarrow{i} + 2 \overrightarrow{j} \right)A\cos\omega t .\]
The motion of the particle is
(a) on a straight line
(b) on an ellipse
(c) periodic
(d) simple harmonic
An object is released from rest. The time it takes to fall through a distance h and the speed of the object as it falls through this distance are measured with a pendulum clock. The entire apparatus is taken on the moon and the experiment is repeated
(a) the measured times are same
(b) the measured speeds are same
(c) the actual times in the fall are equal
(d) the actual speeds are equal
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10 cm and time period 6 s. At t = 0 it is at position x = 5 cm going towards positive x-direction. Write the equation for the displacement x at time t. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle at t = 4 s.
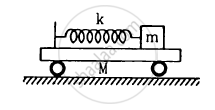
All the surfaces shown in figure are frictionless. The mass of the care is M, that of the block is m and the spring has spring constant k. Initially the car and the block are at rest and the spring is stretched through a length x0 when the system is released. (a) Find the amplitudes of the simple harmonic motion of the block and of the care as seen from the road. (b) Find the time period(s) of the two simple harmonic motions.
Assume that a tunnel is dug along a chord of the earth, at a perpendicular distance R/2 from the earth's centre where R is the radius of the earth. The wall of the tunnel is frictionless. (a) Find the gravitational force exerted by the earth on a particle of mass mplaced in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre of the tunnel. (b) Find the component of this force along the tunnel and perpendicular to the tunnel. (c) Find the normal force exerted by the wall on the particle. (d) Find the resultant force on the particle. (e) Show that the motion of the particle in the tunnel is simple harmonic and find the time period.
A simple pendulum of length l is suspended through the ceiling of an elevator. Find the time period of small oscillations if the elevator (a) is going up with and acceleration a0(b) is going down with an acceleration a0 and (c) is moving with a uniform velocity.
A closed circular wire hung on a nail in a wall undergoes small oscillations of amplitude 20 and time period 2 s. Find (a) the radius of the circular wire, (b) the speed of the particle farthest away from the point of suspension as it goes through its mean position, (c) the acceleration of this particle as it goes through its mean position and (d) the acceleration of this particle when it is at an extreme position. Take g = π2 m/s2.
A particle is subjected to two simple harmonic motions of same time period in the same direction. The amplitude of the first motion is 3.0 cm and that of the second is 4.0 cm. Find the resultant amplitude if the phase difference between the motions is (a) 0°, (b) 60°, (c) 90°.
A particle executing SHM crosses points A and B with the same velocity. Having taken 3 s in passing from A to B, it returns to B after another 3 s. The time period is ____________.
The length of a second’s pendulum on the surface of the Earth is 0.9 m. The length of the same pendulum on the surface of planet X such that the acceleration of the planet X is n times greater than the Earth is
A simple pendulum has a time period T1. When its point of suspension is moved vertically upwards according to as y = kt2, where y is the vertical distance covered and k = 1 ms−2, its time period becomes T2. Then, T `"T"_1^2/"T"_2^2` is (g = 10 ms−2)
Consider the Earth as a homogeneous sphere of radius R and a straight hole is bored in it through its centre. Show that a particle dropped into the hole will execute a simple harmonic motion such that its time period is
T = `2π sqrt("R"/"g")`
Consider a simple pendulum of length l = 0.9 m which is properly placed on a trolley rolling down on a inclined plane which is at θ = 45° with the horizontal. Assuming that the inclined plane is frictionless, calculate the time period of oscillation of the simple pendulum.
A simple harmonic motion is given by, x = 2.4 sin ( 4πt). If distances are expressed in cm and time in seconds, the amplitude and frequency of S.H.M. are respectively,
A spring is stretched by 5 cm by a force of 10 N. The time period of the oscillations when a mass of 2 kg is suspended by it is ______
Motion of a ball bearing inside a smooth curved bowl, when released from a point slightly above the lower point is ______.
- simple harmonic motion.
- non-periodic motion.
- periodic motion.
- periodic but not S.H.M.
A container consist of hemispherical shell of radius 'r ' and cylindrical shell of height 'h' radius of same material and thickness. The maximum value h/r so that container remain stable equilibrium in the position shown (neglect friction) is ______.

