Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the locus of points at distances less than 3 cm from a given point.
Describe the locus of a point at a distance 3 cm from a fixed point.
उत्तर
The locus is the space inside of the circle whose radius is 3 cm and the centre is the fixed point which is given.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In parallelogram ABCD, side AB is greater than side BC and P is a point in AC such that PB bisects angle B. Prove that P is equidistant from AB and BC.
The given figure shows a triangle ABC in which AD bisects angle BAC. EG is perpendicular bisector of side AB which intersects AD at point F.
Prove that:
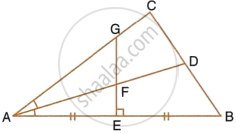
F is equidistant from A and B.
Draw an ∠ABC = 60°, having AB = 4.6 cm and BC = 5 cm. Find a point P equidistant from AB and BC; and also equidistant from A and B.
Describe the locus of a runner, running around a circular track and always keeping a distance of 1.5 m from the inner edge.
Sketch and describe the locus of the vertices of all triangles with a given base and a given altitude.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 6 cm, BC = 4.5 cm and AC = 5 cm. Draw and label:
- the locus of the centres of all circles which touch AB and AC,
- the locus of the centres of all the circles of radius 2 cm which touch AB.
Hence, construct the circle of radius 2 cm which touches AB and AC .
In a quadrilateral PQRS, if the bisectors of ∠ SPQ and ∠ PQR meet at O, prove that O is equidistant from PS and QR.
Find the locus of points which are equidistant from three non-collinear points.
ΔPBC and ΔQBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC but on the opposite sides of line BC. Show that PQ bisects BC at right angles.
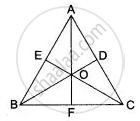
In Fig. AB = AC, BD and CE are the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB respectively such that BD and CE intersect each other at O. AO produced meets BC at F. Prove that AF is the right bisector of BC.