Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between RNA and DNA
उत्तर
| Sr. No. | RNA | DNA |
| 1. | The majority of the RNA is contained in the cytoplasm. | It mainly occurs within the nucleus and specific cell organelles. |
| 2. | Apart from specific viruses, RNA does not serve as the genetic material. | DNA represents the genetic material. |
| 3. | RNA is single-stranded, except in some viruses (e.g., double stranded in Reovirus). | Unlike certain viruses (e.g., Φ × 174), it is double-stranded. |
| 4. | There are at least three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. | There are only two types of DNA: intranuclear and extranuclear. |
| 5. | It contains ribose sugar. | It contains deoxyribose sugar. |
| 6. | Thymine is substituted with uracil in RNA, whereas the other three are similar: adenine, cytosine, and guanine. | Nitrogen bases in DNA include adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. |
| 7. | Many unusual or modified bases are frequently present. | Unusual bases are scarce or nonexistent. |
| 8. | Base pairing via hydrogen bonds occurs exclusively in the coiled portions. | Hydrogen bonds develop between complementary nitrogen bases on the opposite strands of DNA (A-T and C-G). |
| 9. | The strand may fold at points to form a secondary helix or pseudohelix. | DNA is spirally twisted to form a regular helix. |
| 10. | It cannot usually reproduce itself. | It replicates to produce new DNA molecules. |
| 11. | RNA transforms the transcribed message into polypeptides. | DNA transcribes genetic information into RNA. |
| 12. | The quantity of RNA of a cell is variable. | The quantity is fixed for each cell. |
| 13. | There is no association between the number of purine and pyrimidine bases. | There are an equal number of purine and pyrimidine bases. |
| 14. | It exists in ribosomes or establishes a connection with them. | It takes the form of prochromosome, chromatin, or chromosomes. |
| 15. | Some RNAs are extremely short-lived, whereas others are slightly longer. | It is long-lived. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Rearrange the following in the correct sequence to accomplish an important biological reaction:
(a) In vitro synthesis of copies of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of ds-DNA
What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell?
One of the major contributions of biotechnology is to develop pest-resistant varieties of cotton plants. Explain how it has been made possible.
What are the restriction endonucleases? Give the rules of their nomenclature.
Enlist different types of restriction enzymes commonly used in rDNA technology? Write about their role.
Define vector? write any two examples,
Identify the palindromic sequence which is recognized by the EcoRI restriction enzyme.
From the following which one is NOT a feature of the plasmids?
For which of the following purpose restriction endonuclease enzyme is used in genetic engineering?
The time taken to complete one cycle of PCR is around ______.
Which of the following is an INCORRECT match?
Consider there is only one double stranded DNA molecule initially along with all other requirements of PCR. If a PCR machines performs 10 cycles of reaction then bow many double stranded DNA molecules would be present at the end?
Study the following statements regarding separation of DNA using agarose gel electrophoresis.
- Large fragments of DNA molecules move faster than small DNA fragments and thus separate faster.
- DNA being negatively charged migrates to cathode.
____________ is the manipulation of genetic material towards a desired end, in a directed and predetermined way, using in vitro process.
Which of the following viruses has the capacity to produce lysozymes?
What is meant by gene cloning?
Cloning of genes, play a very significant role in genetic engineering, helping the transfer of desirable foreign genes into different hosts. The scientists, to make this process easier and effective are creating engineered vectors in such a way that they help easy linking of foreign DNA and selection of recombinants from non-recombinants. 'pBR322' is one such engineered vectors developed by scientists. A diagram of an engineered vector pBR322 is given below:
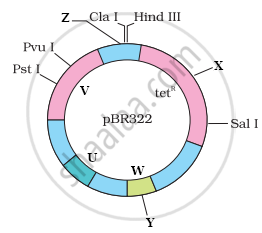
- Name the host for this cloning vector.
- Identify 'Rop' and 'Ori' in the diagram from 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y' and 'Z'. Write their functions.
- Draw the fragments that will be formed by the action of 'Z' (marked in the diagram) on the specific site of the DNA segment given below:
5' --- GTACGAATCCTGA --- 3'
3' --- CATGCTTAGGACT --- 3'
pBR322, used very frequently in cloning experiments as a vector in E. coli is ______.
Importance of PCR.
In vitro amplification of DNA segments is called______.
