Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a circle of radius 6 cm. In the circle, draw a chord AB = 6 cm.
(i) If O is the center of the circle, join OA and OB.
(ii) Assign a special name to ∆AOB
(iii) Write the measure of angle AOB.
उत्तर
(i)
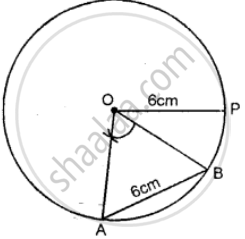
(ii) Δ AOB is equilateral triangle.
(iii) By measurement ∠AOB = 60°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
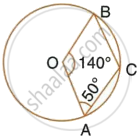
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠AOB = 140° and ∠OAC = 50°; find:
- ∠ACB,
- ∠OBC,
- ∠OAB,
- ∠CBA.
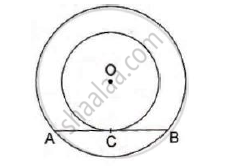
In the given figure, the chord AB of the larger of the two concentric circles, with center O, touches the smaller circle at C. Prove that AC = CB.
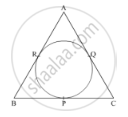
In Fig. 4, an isosceles triangle ABC, with AB = AC, circumscribes a circle. Prove that the point of contact P bisects the base BC.
The longest chord of a circle is __________
In the figure, a circle touches all the sides of quadrilateral ABCD from the inside. The center of the circle is O. If AD⊥ DC and BC = 38, QB = 27, DC = 25, then find the radius of the circle.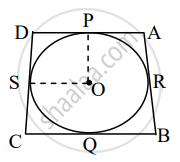
If the angle between two tangents drawn from a point P to a circle of radius ‘a’ and centre ‘O’ is 90°, then OP = ______
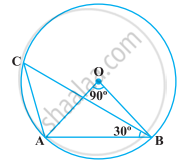
In the following figure, ∠AOB = 90º and ∠ABC = 30º, then ∠CAO is equal to ______.
Is every chord of a circle also a diameter?
Find the length of the arc of a circle which subtends an angle of 60° at the centre of the circle of radius 42 cm.
Assertion (A): If the circumference of a circle is 176 cm, then its radius is 28 cm.
Reason (R): Circumference = 2π × radius of a circle.
