Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a circle of radius 6 cm. In the circle, draw a chord AB = 6 cm.
(i) If O is the center of the circle, join OA and OB.
(ii) Assign a special name to ∆AOB
(iii) Write the measure of angle AOB.
उत्तर
(i)
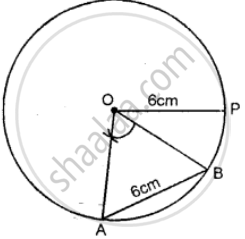
(ii) Δ AOB is equilateral triangle.
(iii) By measurement ∠AOB = 60°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the fig. ABC is right triangle right angled at B such that BC = 6cm and AB = 8cm. Find the radius of its in circle.
From an external point P , tangents PA = PB are drawn to a circle with centre O . If \[\angle PAB = {50}^o\] , then find \[\angle AOB\]
In the following figure, OABC is a square. A circle is drawn with O as centre which meets OC at P and OA at Q.
Prove that:
( i ) ΔOPA ≅ ΔOQC
( ii ) ΔBPC ≅ ΔBQA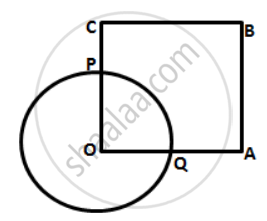
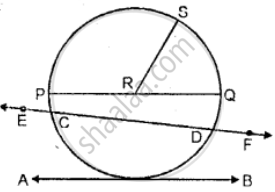
Use the figure given below to fill in the blank:
R is the _______ of the circle.
Construct a triangle PQR in which, PQ = QR = RP = 5.7 cm. Draw the incircle of the triangle and measure its radius.
Draw circle with the radii given below.
4 cm
Given: A circle inscribed in a right angled ΔABC. If ∠ACB = 90° and the radius of the circle is r.
To prove: 2r = a + b – c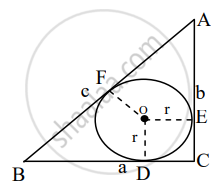
Two circles with centres O and O' of radii 3 cm and 4 cm, respectively intersect at two points P and Q such that OP and O'P are tangents to the two circles. Find the length of the common chord PQ.
In the following figure, ∠OAB = 30º and ∠OCB = 57º. Find ∠BOC and ∠AOC.

From the figure, identify a point in the exterior.