Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a circle of radius 4.8 cm and mark its center as P.
(i) Draw radii PA and PB such that ∠APB = 45°.
(ii) Shade the major sector of the circle
उत्तर
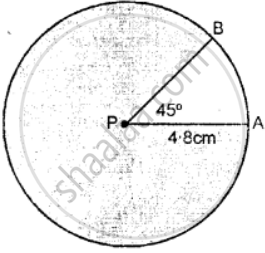
PA is the radius of the circle. i.c., PA = 4.8 cm.
(i) ∠APB = 45° in which P is the center of the circle and PA and PB are radii of the circle.
(ii) The major sector of the circle is shaded in the above figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that in two concentric circles, the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle, is bisected at the point of contact.
Write True or False. Give reason for your answer.
Line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
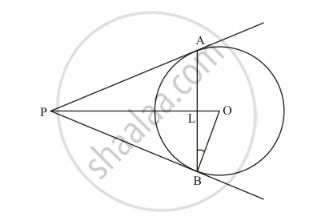
In the given figure, AB is a chord of length 16 cm of a circle of radius 10 cm. The tangents at A and B intersect at a point P. Find the length of PA.
Find the length of the chord of a circle in the following when:
Radius is 13 cm and the distance from the centre is 12 cm
Circles with centres A, B and C touch each other externally. If AB = 3 cm, BC = 3 cm, CA = 4 cm, then find the radii of each circle.
From a point P which is at a distance of 13 cm from the centre O of a circle of radius 5 cm, the pair of tangents PQ and PR to the circle are drawn. Then the area of the quadrilateral PQOR is ______
AB and AC are two equal chords of a circle. Prove that the bisector of the angle BAC passes through the centre of the circle.
If a line segment joining mid-points of two chords of a circle passes through the centre of the circle, prove that the two chords are parallel.
On a common hypotenuse AB, two right triangles ACB and ADB are situated on opposite sides. Prove that ∠BAC = ∠BDC.
A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle such that AB is a diameter and ∠ADC = 130º. Find ∠BAC.
