Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - "e"^(-x))/sinx`
उत्तर
We know `lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - 1)/x` = 1
`lim_(x -> 0) sinx/x` = 1
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - "e"^(-x))/sinx = lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - 1/"e"^x)/sinx`
= `lim_(x -> 0) (("e"^x * "e"^x - 1)/"e"^x)/(sinx)`
= `lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^(2x) - 1)/("e"^x sinx)`
= `lim_(x -> 0) (1/"e"^x xx ("e"^(2x) - 1)/(1/2 xx 2x) xx x/sinx)`
= `(lim_(x -> 0) 1/"e"^x) 2(lim_(2x -> 0) ("e"^(2x) - 1)/(2x)) xx 1/((lim_(x -> 0) sinx/x))`
= `1/"e"^0 xx 2 xx 1 xx 1/1`
= `1/1 xx 2 xx 1`
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - "e"^(-x))/sinx` = 2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Evaluate the following limit:
`lim_(z -> -3) [sqrt("z" + 6)/"z"]`
Evaluate the following limit:
`lim_(x -> 3)[sqrt(2x + 6)/x]`
Evaluate the following limit :
`lim_(x -> 7)[((root(3)(x) - root(3)(7))(root(3)(x) + root(3)(7)))/(x - 7)]`
Evaluate the following limit :
If `lim_(x -> 5) [(x^"k" - 5^"k")/(x - 5)]` = 500, find all possible values of k.
In the following example, given ∈ > 0, find a δ > 0 such that whenever, |x – a| < δ, we must have |f(x) – l| < ∈.
`lim_(x -> 2)(2x + 3)` = 7
In the following example, given ∈ > 0, find a δ > 0 such that whenever, |x – a| < δ, we must have |f(x) – l| < ∈.
`lim_(x -> 1) (x^2 + x + 1)` = 3
Evaluate the following :
`lim_(x -> 1) [(x + 3x^2 + 5x^3 + ... + (2"n" - 1)x^"n" - "n"^2)/(x - 1)]`
In exercise problems 7 – 15, use the graph to find the limits (if it exists). If the limit does not exist, explain why?
`lim_(x -> x/2) tan x`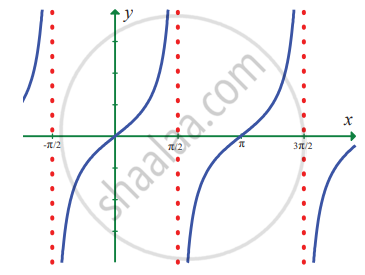
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 2) (x^4 - 16)/(x - 2)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(x^2 + 1) - 1)/(sqrt(x^2 + 16) - 4)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(1 - x) - 1)/x^2`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> oo) (x^3 + x)/(x^4 - 3x^2 + 1)`
A tank contains 5000 litres of pure water. Brine (very salty water) that contains 30 grams of salt per litre of water is pumped into the tank at a rate of 25 litres per minute. The concentration of salt water after t minutes (in grams per litre) is C(t) = `(30"t")/(200 + "t")`. What happens to the concentration as t → ∞?
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0)(1 + x)^(1/(3x))`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (1 - cos^2x)/(x sin2x)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> oo) x [3^(1/x) + 1 - cos(1/x) - "e"^(1/x)]`
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x -> oo) (1/"n"^2 + 2/"n"^2 + 3/"n"^2 + ... + "n"/"n"^2)` is
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^(sin x) - 1)/x` =
`lim_(x -> 0) ((2 + x)^5 - 2)/((2 + x)^3 - 2)` = ______.
