Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill the blank in the following so that the following statement is true.
Sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are ......
उत्तर
Sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two lines AB and CD intersect at O such that BC is equal and parallel to AD. Prove that the lines AB and CD bisect at O.
Find the measure of each exterior angle of an equilateral triangle.
BD and CE are bisectors of ∠B and ∠C of an isosceles ΔABC with AB = AC. Prove that BD = CE.
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The bisectors of two equal angles of a triangle are equal
Is it possible to draw a triangle with sides of length 2 cm, 3 cm and 7 cm?
ABC is a triangle. The bisector of the exterior angle at B and the bisector of ∠C intersect each other at D. Prove that ∠D = \[\frac{1}{2}\] ∠A.
Write the sum of the angles of an obtuse triangle.
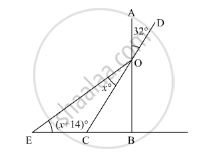
In the given figure, if AB ⊥ BC. then x =
ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC and D is a point on BC such that AD ⊥ BC (Figure). To prove that ∠BAD = ∠CAD, a student proceeded as follows:
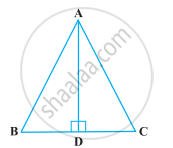
In ∆ABD and ∆ACD,
AB = AC (Given)
∠B = ∠C (Because AB = AC)
and ∠ADB = ∠ADC
Therefore, ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACD (AAS)
So, ∠BAD = ∠CAD (CPCT)
What is the defect in the above arguments?
[Hint: Recall how ∠B = ∠C is proved when AB = AC].
Show that in a quadrilateral ABCD, AB + BC + CD + DA > AC + BD
