Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the equation of the straight line upon which the length of the perpendicular from the origin is 2 and the slope of this perpendicular is \[\frac{5}{12}\].
उत्तर
Let the perpendicular drawn from the origin make acute angle \[\alpha\] with the positive x-axis.
Then, we have,
\[\text { tan }\alpha = \frac{5}{12}\]
Here,
\[\tan\left( {180}^\circ + \alpha \right) = \text { tan }\alpha\]
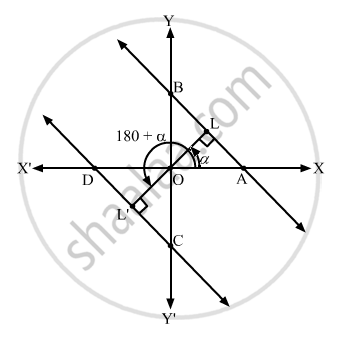
\[\text { Now }, tan\alpha = \frac{5}{12}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text { sin }\alpha = \frac{5}{13} \text { and cos }\alpha = \frac{12}{13}\]
Here, p = 2
So, the equations of the lines in normal form are
\[x\text {cos }\alpha + y\text { sin }\alpha = p \text { and } x\cos\left( {180}^\circ + \alpha \right) + y\text { sin }\left( {180}^\circ + \alpha \right) = p\]
\[ \Rightarrow x\text { cos }\alpha + y\text { sin }\alpha = 2 \text { and} - \text { x cos }\alpha - ysin\alpha = 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{12x}{13} + \frac{5y}{13} = 2 \text { and } - \frac{12x}{13} - \frac{5y}{13} = 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12x + 5y = 26 \text { and } 12x + 5y = - 26\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Reduce the following equation into intercept form and find their intercepts on the axes.
3y + 2 = 0
Reduce the following equation into normal form. Find their perpendicular distances from the origin and angle between perpendicular and the positive x-axis.
`x – sqrt3y + 8 = 0`
Find equation of the line parallel to the line 3x – 4y + 2 = 0 and passing through the point (–2, 3).
Prove that the product of the lengths of the perpendiculars drawn from the points `(sqrt(a^2 - b^2), 0)` and `(-sqrta^2-b^2, 0)` to the line `x/a cos theta + y/b sin theta = 1` is `b^2`.
A person standing at the junction (crossing) of two straight paths represented by the equations 2x – 3y+ 4 = 0 and 3x + 4y – 5 = 0 wants to reach the path whose equation is 6x – 7y + 8 = 0 in the least time. Find equation of the path that he should follow.
Find the equation of a line making an angle of 150° with the x-axis and cutting off an intercept 2 from y-axis.
Find the equation of a line which makes an angle of tan−1 (3) with the x-axis and cuts off an intercept of 4 units on negative direction of y-axis.
Find the lines through the point (0, 2) making angles \[\frac{\pi}{3} \text { and } \frac{2\pi}{3}\] with the x-axis. Also, find the lines parallel to them cutting the y-axis at a distance of 2 units below the origin.
Find the equation of the bisector of angle A of the triangle whose vertices are A (4, 3), B (0, 0) and C(2, 3).
Find the equations of the diagonals of the square formed by the lines x = 0, y = 0, x = 1 and y =1.
Point R (h, k) divides a line segment between the axes in the ratio 1 : 2. Find the equation of the line.
Find the equation of a line for p = 8, α = 300°.
Find the value of θ and p, if the equation x cos θ + y sin θ = p is the normal form of the line \[\sqrt{3}x + y + 2 = 0\].
Reduce the following equation to the normal form and find p and α in \[x + \sqrt{3}y - 4 = 0\] .
Show that the origin is equidistant from the lines 4x + 3y + 10 = 0; 5x − 12y + 26 = 0 and 7x + 24y = 50.
Find the coordinates of the vertices of a triangle, the equations of whose sides are x + y − 4 = 0, 2x − y + 3 = 0 and x − 3y + 2 = 0.
Find the area of the triangle formed by the line y = m1 x + c1, y = m2 x + c2 and x = 0.
Find the orthocentre of the triangle the equations of whose sides are x + y = 1, 2x + 3y = 6 and 4x − y + 4 = 0.
If the lines p1 x + q1 y = 1, p2 x + q2 y = 1 and p3 x + q3 y = 1 be concurrent, show that the points (p1, q1), (p2, q2) and (p3, q3) are collinear.
Find the equation of the straight line which has y-intercept equal to \[\frac{4}{3}\] and is perpendicular to 3x − 4y + 11 = 0.
Find the values of the parameter a so that the point (a, 2) is an interior point of the triangle formed by the lines x + y − 4 = 0, 3x − 7y − 8 = 0 and 4x − y − 31 = 0.
Write the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle formed by the lines x2 − y2 = 0 and x + 6y = 18.
If a ≠ b ≠ c, write the condition for which the equations (b − c) x + (c − a) y + (a − b) = 0 and (b3 − c3) x + (c3 − a3) y + (a3 − b3) = 0 represent the same line.
The point which divides the join of (1, 2) and (3, 4) externally in the ratio 1 : 1
If the lines ax + 12y + 1 = 0, bx + 13y + 1 = 0 and cx + 14y + 1 = 0 are concurrent, then a, b, c are in
The equations of the sides AB, BC and CA of ∆ ABC are y − x = 2, x + 2y = 1 and 3x + y + 5 = 0 respectively. The equation of the altitude through B is
The figure formed by the lines ax ± by ± c = 0 is
Find the equation of a line which passes through the point (2, 3) and makes an angle of 30° with the positive direction of x-axis.
Find the equation of the line where length of the perpendicular segment from the origin to the line is 4 and the inclination of the perpendicular segment with the positive direction of x-axis is 30°.
The inclination of the line x – y + 3 = 0 with the positive direction of x-axis is ______.
A line passes through P(1, 2) such that its intercept between the axes is bisected at P. The equation of the line is ______.
For specifying a straight line, how many geometrical parameters should be known?
The line which cuts off equal intercept from the axes and pass through the point (1, –2) is ______.
Locus of the mid-points of the portion of the line x sin θ + y cos θ = p intercepted between the axes is ______.
Reduce the following equation into slope-intercept form and find their slopes and the y-intercepts.
6x + 3y – 5 = 0
