Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the vector and the Cartesian equations of the line that passes through the points (3, −2, −5), (3, −2, 6).
उत्तर
Let the line passing through the points, P (3, −2, −5) and Q (3, −2, 6), be PQ.
Since PQ passes through P (3, −2, −5), its position vector is given by,
`veca = 3hati -2hatj - 5hatk`
The direction ratios of PQ are given by,
(3 − 3) = 0, (−2 + 2) = 0, (6 + 5) = 11
The equation of the vector in the direction of PQ is
`vecb = 0.hati - 0.hatj + 11hatk = 11hatk`
The equation of PQ in vector form is given by, `vecr = veca + lambdavecb`, `lambda in R`
`=>vecr = (3hati - 2hatj - 5hatk) + 11lambdahatk`
The equation of PQ in Cartesian form is
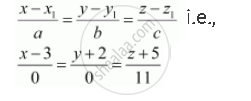
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the vector and cartesian equations of the line passing through the point (2, 1, 3) and perpendicular to the lines
`(x-1)/1=(y-2)/2=(z-3)/3 and x/(-3)=y/2=z/5`
Show that the line through the points (4, 7, 8) (2, 3, 4) is parallel to the line through the points (−1, −2, 1), (1, 2, 5).
Find the Cartesian equation of the line which passes through the point (−2, 4, −5) and parallel to the line given by `(x+3)/3 = (y-4)/5 = (z+8)/6`.
Find the vector and cartesian equations of the line through the point (5, 2, −4) and which is parallel to the vector \[3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - 8 \hat{k} .\]
Find the vector equation of a line which is parallel to the vector \[2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k}\] and which passes through the point (5, −2, 4). Also, reduce it to cartesian form.
Find the vector equation of a line passing through (2, −1, 1) and parallel to the line whose equations are \[\frac{x - 3}{2} = \frac{y + 1}{7} = \frac{z - 2}{- 3} .\]
Find the direction cosines of the line \[\frac{4 - x}{2} = \frac{y}{6} = \frac{1 - z}{3} .\] Also, reduce it to vector form.
Show that the points whose position vectors are \[- 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} , \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \text{ and } 7 \text{ i} - \text{ k} \] are collinear.
Find the cartesian and vector equations of a line which passes through the point (1, 2, 3) and is parallel to the line \[\frac{- x - 2}{1} = \frac{y + 3}{7} = \frac{2z - 6}{3} .\]
Show that the line through the points (1, −1, 2) and (3, 4, −2) is perpendicular to the through the points (0, 3, 2) and (3, 5, 6).
Find the angle between the following pair of line:
\[\frac{- x + 2}{- 2} = \frac{y - 1}{7} = \frac{z + 3}{- 3} \text{ and } \frac{x + 2}{- 1} = \frac{2y - 8}{4} = \frac{z - 5}{4}\]
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (2, −1, 3) and parallel to the line \[\overrightarrow{r} = \left( \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right) + \lambda\left( 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} \right) .\]
Show that the lines \[\frac{x - 5}{7} = \frac{y + 2}{- 5} = \frac{z}{1} \text{ and } \frac{x}{1} = \frac{y}{2} = \frac{z}{3}\] are perpendicular to each other.
Find the direction cosines of the line
\[\frac{x + 2}{2} = \frac{2y - 7}{6} = \frac{5 - z}{6}\] Also, find the vector equation of the line through the point A(−1, 2, 3) and parallel to the given line.
Show that the lines \[\frac{x + 1}{3} = \frac{y + 3}{5} = \frac{z + 5}{7} \text{ and } \frac{x - 2}{1} = \frac{y - 4}{3} = \frac{z - 6}{5}\] intersect. Find their point of intersection.
Prove that the lines through A (0, −1, −1) and B (4, 5, 1) intersects the line through C (3, 9, 4) and D (−4, 4, 4). Also, find their point of intersection.
Show that the lines \[\vec{r} = 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} + \lambda\left( \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) \text{ and } \vec{r} = 5 \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + \mu\left( 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} \right)\] are intersecting. Hence, find their point of intersection.
Find the distance of the point (2, 4, −1) from the line \[\frac{x + 5}{1} = \frac{y + 3}{4} = \frac{z - 6}{- 9}\]
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines whose vector equations are: \[\vec{r} = 3 \hat{i} + 8 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} + \lambda\left( 3 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right) \text{ and } \vec{r} = - 3 \hat{i} - 7 \hat{j} + 6 \hat{k} + \mu\left( - 3 \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k} \right)\]
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines whose vector equations are: \[\overrightarrow{r} = \left( \lambda - 1 \right) \hat{i} + \left( \lambda + 1 \right) \hat{j} - \left( 1 + \lambda \right) \hat{k} \text{ and } \overrightarrow{r} = \left( 1 - \mu \right) \hat{i} + \left( 2\mu - 1 \right) \hat{j} + \left( \mu + 2 \right) \hat{k} \]
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines whose vector equations are: \[\overrightarrow{r} = \left( 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} - \hat{k} \right) + \lambda\left( 2 \hat{i} - 5 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) \text{ and }, \overrightarrow{r} = \left( \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right) + \mu\left( \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right)\]
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines whose cartesian equations are : \[\frac{x - 1}{2} = \frac{y + 1}{3} = z \text{ and } \frac{x + 1}{3} = \frac{y - 2}{1}; z = 2\]
By computing the shortest distance determine whether the following pairs of lines intersect or not: \[\frac{x - 5}{4} = \frac{y - 7}{- 5} = \frac{z + 3}{- 5} \text{ and } \frac{x - 8}{7} = \frac{y - 7}{1} = \frac{z - 5}{3}\]
Write the coordinate axis to which the line \[\frac{x - 2}{3} = \frac{y + 1}{4} = \frac{z - 1}{0}\] is perpendicular.
Write the angle between the lines \[\frac{x - 5}{7} = \frac{y + 2}{- 5} = \frac{z - 2}{1} \text{ and } \frac{x - 1}{1} = \frac{y}{2} = \frac{z - 1}{3} .\]
Write the angle between the lines 2x = 3y = −z and 6x = −y = −4z.
The equations of a line are given by \[\frac{4 - x}{3} = \frac{y + 3}{3} = \frac{z + 2}{6} .\] Write the direction cosines of a line parallel to this line.
The lines `x/1 = y/2 = z/3 and (x - 1)/-2 = (y - 2)/-4 = (z - 3)/-6` are
If the direction ratios of a line are proportional to 1, −3, 2, then its direction cosines are
The equation of a line is 2x -2 = 3y +1 = 6z -2 find the direction ratios and also find the vector equation of the line.
Find the value of λ for which the following lines are perpendicular to each other:
`(x - 5)/(5 lambda + 2 ) = ( 2 - y )/5 = (1 - z ) /-1 ; x /1 = ( y + 1/2)/(2 lambda ) = ( z -1 ) / 3`
If y – 2x – k = 0 touches the conic 3x2 – 5y2 = 15, find the value of k.
Find the value of λ, so that the lines `(1-"x")/(3) = (7"y" -14)/(λ) = (z -3)/(2) and (7 -7"x")/(3λ) = ("y" - 5)/(1) = (6 -z)/(5)` are at right angles. Also, find whether the lines are intersecting or not.
Choose correct alternatives:
If the equation 4x2 + hxy + y2 = 0 represents two coincident lines, then h = _______
Choose correct alternatives:
The difference between the slopes of the lines represented by 3x2 - 4xy + y2 = 0 is 2
The distance of the point (4, 3, 8) from the Y-axis is ______.
Find the position vector of a point A in space such that `vec"OA"` is inclined at 60º to OX and at 45° to OY and `|vec"OA"|` = 10 units.
Find the cartesian equation of the line which passes ·through the point (– 2, 4, – 5) and parallel to the line given by.
`(x + 3)/3 = (y - 4)/5 = (z + 8)/6`
Find the equations of the diagonals of the parallelogram PQRS whose vertices are P(4, 2, – 6), Q(5, – 3, 1), R(12, 4, 5) and S(11, 9, – 2). Use these equations to find the point of intersection of diagonals.
