Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names.
- Classify the isomers of alcohols in the above question as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
उत्तर
i. The isomeric alcohols with molecular formula C5H12O are –
(a) \[\ce{\underset{Pentanol (1^\circ)}{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - OH}}\]
(b) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - \overset{∗}{C}H - CH3}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\phantom{...............}\ce{\underset{Pentan-2-ol (2^\circ)}{OH}}\
\end{array}\]
(c) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{\underset{Pentan-3-ol (2^\circ)}{OH}}\
\end{array}\]
(d) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H3C - H2C - H\overset{∗}{C} - CH2OH}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{.........}\ce{\underset{2-Methylbutan-1-ol (1^\circ)}{CH3}}\
\end{array}\]
(e) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{............}\\
|\phantom{...............}\\
\ce{\underset{3-Methylbutan-1-ol (1^\circ)}{CH3 - CH - CH2 - CH2 - OH}}\\
\end{array}\]
(f) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\
|\phantom{.......}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{.......}\\
\ce{\underset{2-Methylbutan-2-ol (3^\circ)}{OH}}\phantom{....}\
\end{array}\]
(g) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - OH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{2, 2-Dimethylpropan-1-ol (1^\circ)}{CH3}}\phantom{..}\
\end{array}\]
(h) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{\underset{3-Methylbutan-2-ol (2^\circ)}{CH3 - CH - \underset{∗}{C}H - CH3}}\
\end{array}\]
Isomers (b), (d) and (h) contain chiral carbon atoms; thus, they exhibit enantiomerism.
ii. Isomers (a), (d), (e) and (g) are primary alcohols.
Isomers (b), (c) and (h) are secondary alcohols.
Isomer (f) is a tertiary alcohol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - C = C - CH2OH}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{Br}\phantom{...}
\end{array}\]
How is phenol converted into the following?
benzene
Give reasons Fluoride ion has higher hydration enthalpy than chloride ion.
Glycerol is ____________.
Butane-2-ol is ____________.
Which of the following compounds is oxidised to prepare methyl ethyl ketone?
1-Propanol and 2-propanol can be best distinguished by:
Which of the following gives a positive iodoform test?
Among the following sets of reactants which one produces anisole?
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ______.
Match the starting materials given in Column I with the products formed by these (Column II) in the reaction with HI.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | CH3—O—CH3 | (a) | 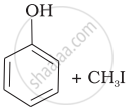 |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.............}\\ \ce{CH-O-CH3}\\ /\phantom{..............}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................} \end{array}\] |
(b) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-I + CH3OH}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{H3C-C-O-CH3}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..} \end{array}\] |
(c) | 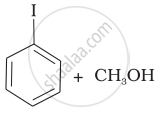 |
| (iv) | 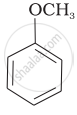 |
(d) | CH3—OH + CH3—I |
| (e) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-OH + CH3I}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (f) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-I + CH3OH}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (g) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-OH + CH3I}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
Assertion: Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium yields butan-1-ol.
Reason: Addition of water in acidic medium proceeds through the formation of primary carbocation.
Assertion: IUPAC name of the compound
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - O - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\] is 2-Ethoxy-2-methylethane.
Reason: In IUPAC nomenclature, ether is regarded as hydrocarbon derivative in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by —OR or —OAr group [where R = alkyl group and Ar = aryl group]
Assertion: Like bromination of benzene, bromination of phenol is also carried out in the presence of Lewis acid.
Reason: Lewis acid polarises the bromine molecule.
Write complete reaction for the bromination of phenol in aqueous and non-aqueous medium.
How can phenol be converted to aspirin?
How are the following conversions carried out?
Methyl magnesium bromide→2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
Give the structures of Thiosulphuric acid and Peroxy monosulphuric acid.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
