Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If n = 3, what are the quantum number l and m?
उत्तर
For a given n, l = 0 to (n − 1) and forgiven l, ml = −l...., 0, ..... + l
Therefore, the possible values of l and ml for n = 3 are:
| Value of n | Value of l | Values of ml |
| 3 | 0 | ml = 0 |
| 1 | ml = −1 ml = 0 ml = +1 |
|
| 2 | ml = −2 ml = −1 ml = 0 ml = +1 ml = +2 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
p-orbitals are _________ in shape.
Choose the correct option.
“No two electrons in the same atoms can have identical set of four quantum numbers”. This statement is known as -
Choose the correct option.
Principal Quantum number describes -
Define the term Electronic configuration
State Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity with a suitable example.
Explain the anomalous behaviour of copper.
Explain the anomalous behaviour of chromium.
Write electronic configurations of \[\ce{Fe, Fe2+, Fe3+}\].
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Lithium (Z = 3)
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Oxygen (Z = 8)
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Silicon (Z = 14)
Draw shapes of 2p orbitals.
Explain in brief, the significance of the azimuthal quantum number.
The electronic configuration of oxygen is written as 1s2 2s2 \[\ce{2p^2_{{x}}}\] \[\ce{2p^1_{{y}}}\] \[\ce{2p^1_{{z}}}\] and not as 1s2 2s2 \[\ce{2p^2_{{x}}}\], \[\ce{2p^2_{{y}}}\] \[\ce{2p^0_{{z}}}\], Explain.
Which mineral among the following contains vanadium in it?
How many electrons can fit in the orbital for which n = 4 and l = 2?
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
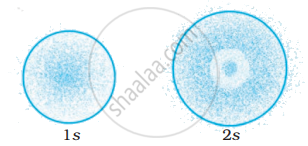
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals:
| (i) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = -1, m_s = - 1/2` | |
| (ii) | (a) `n = 3, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iii) | (a) `n = 4, l = 1, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = 1, m_s = + 1/2` | |
| (iv) | (a) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = - 1/2` |
| (b) `n = 3, l = 2, m_l = +2, m_s = + 1/2` |
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) \[\ce{Na^{+}, Mg^{2+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Al3^{+}, O-}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Na+ , O2-}\]
(iv) \[\ce{N3-, Cl-}\]
Which of the following orbitals are degenerate?
3dxy, 4dxy 3dz2, 3dyz, 4dyz, 4dz2
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, solve the questions given below:
Which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
5p, 5d, 5f, 6s, 6p
Match the following
| (i) Photon | (a) Value is 4 for N shell |
| (ii) Electron | (b) Probability density |
| (iii) ψ2 | (c) Always positive value |
| (iv) Principal quantum number n | (d) Exhibits both momentum and wavelength |
Match species given in Column I with the electronic configuration given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{Cr}\] | (a) [Ar]3d84s0 |
| (ii) \[\ce{Fe^{2+}}\] | (b) [Ar]3d104s1 |
| (iii) \[\ce{Ni^{2+}}\] | (c) [Ar]3d64s0 |
| (iv) \[\ce{Cu}\] | (d) [Ar] 3d54s1 |
| (e) [Ar]3d64s2 |
Choose the INCORRECT statement
Which of the following is the correct plot for the probability density ψ2 (r) as a function of distance 'r' of the electron from the nucleus for 2s orbitals?
In the case of R, S configuration the group having the highest priority is ______.
Which one of the following laws will represent the pairing of electrons in a subshell after each orbital is filled with one electron?
