Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and the vertex is (2, – 1), then find the length of the side of the triangle.
उत्तर
Equation of the base AB of a ΔABC is x + y = 2
In ΔABD,
sin 60° = `"AD"/"AB"`
⇒ `sqrt(3)/2 = "AD"/"AB"`
⇒ AD = `sqrt(3)/2 "AB"`
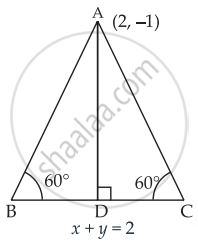
Length of perpendicular from A(2, – 1) to the line x + y = 2 is
AD = `|(1 xx 2 + 1 xx -1 - 2)/sqrt((1)^2 + (1)^2)|`
⇒ `sqrt(3)/2 "AB" = |(2 - 1 - 2)/sqrt(2)| = |(-1)/sqrt(2)|`
⇒ `sqrt(3)/2 "AB" = 1/sqrt(2)`
⇒ AB = `sqrt(2)/sqrt(2)`
Hence, the required length of side = `sqrt(2/3)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the slope of a line, which passes through the origin, and the mid-point of the line segment joining the points P (0, –4) and B (8, 0).
Without using distance formula, show that points (–2, –1), (4, 0), (3, 3) and (–3, 2) are vertices of a parallelogram.
A line passes through (x1, y1) and (h, k). If slope of the line is m, show that k – y1 = m (h – x1).
Find the equation of a line drawn perpendicular to the line `x/4 + y/6 = 1`through the point, where it meets the y-axis.
Find the value of p so that the three lines 3x + y – 2 = 0, px + 2y – 3 = 0 and 2x – y – 3 = 0 may intersect at one point.
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis: \[\frac{\pi}{3}\]
Find the slope of a line passing through the following point:
\[(a t_1^2 , 2 a t_1 ) \text { and } (a t_2^2 , 2 a t_2 )\]
Using the method of slope, show that the following points are collinear A (16, − 18), B (3, −6), C (−10, 6) .
What can be said regarding a line if its slope is zero ?
What can be said regarding a line if its slope is positive ?
Show that the line joining (2, −3) and (−5, 1) is parallel to the line joining (7, −1) and (0, 3).
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: \[\frac{a}{h} + \frac{b}{k} = 1\].
Find the value of x for which the points (x, −1), (2, 1) and (4, 5) are collinear.
Find the angle between X-axis and the line joining the points (3, −1) and (4, −2).
Find the equations of the straight lines which cut off an intercept 5 from the y-axis and are equally inclined to the axes.
Find the equations of the altitudes of a ∆ ABC whose vertices are A (1, 4), B (−3, 2) and C (−5, −3).
The line through (h, 3) and (4, 1) intersects the line 7x − 9y − 19 = 0 at right angle. Find the value of h.
Find the image of the point (3, 8) with respect to the line x + 3y = 7 assuming the line to be a plane mirror.
Find the angles between the following pair of straight lines:
3x + 4y − 7 = 0 and 4x − 3y + 5 = 0
The angle between the lines 2x − y + 3 = 0 and x + 2y + 3 = 0 is
The equation of the line with slope −3/2 and which is concurrent with the lines 4x + 3y − 7 = 0 and 8x + 5y − 1 = 0 is
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (2, 3) on the line x + y − 11 = 0 are
The reflection of the point (4, −13) about the line 5x + y + 6 = 0 is
If the slopes of the lines given by the equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 are in the ratio 5 : 3, then the ratio h2 : ab = ______.
Point of the curve y2 = 3(x – 2) at which the normal is parallel to the line 2y + 4x + 5 = 0 is ______.
Find the angle between the lines y = `(2 - sqrt(3)) (x + 5)` and y = `(2 + sqrt(3))(x - 7)`
The three straight lines ax + by = c, bx + cy = a and cx + ay = b are collinear, if ______.
