Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 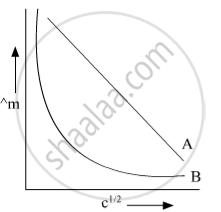
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
उत्तर
Electrolyte A is strong electrolyte & Electrolyte B is weak electrolyte On extrapolation of Λm to concentration approaching zero for strong electrolytes, we get the value of Λ=m i.e. molar conductance at infinite dilution In the case of weak electrolytes, Λm increases steeply on dilution. Therefore, Λ=m cannot be obtained by extrapolation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and if `∧_"m"^0` for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what is its dissociation constant?
The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is __________.
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes because of the fact that ____________.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
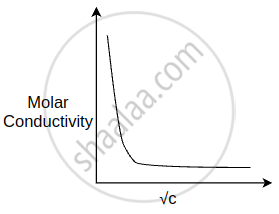
The electrolyte X is ______.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
