Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is said that a liquid rises or is depressed in capillary due to the surface tension. If a liquid neither rises nor depresses in a capillary, can we conclude that the surface tension of the liquid is zero?
उत्तर
No, we cannot conclude the surface tension to be zero solely by the fact that the liquid neither rises nor falls in a capillary.
The height of the liquid inside a capillary tube is given by \[h = \frac{2T\cos\theta}{r\rho g}\] . From the equation, we see that the height (h) of the liquid may also be zero if the contact angle \[\theta\] between the liquid and the capillary tube is \[{90}^0 \text{ or } {270}^0\] .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
The total free surface energy of a liquid drop is `pisqrt2` times the surface tension of the liquid. Calculate the diameter of the drop in S.l. unit.
The free surface of a liquid resting in an inertial frame is horizontal. Does the normal to the free surface pass through the centre of the earth? Think separately if the liquid is (a) at the equator (b) at a pole (c) somewhere else.
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
Find the excess pressure inside (a) a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm (b) a soap bubble of radius 4 mm and (c) an air bubble of radius 4 mm formed inside a tank of water. Surface tension of mercury, soap solution and water are 0.465 N m−1, 0.03 N m−1 and 0.076 N m−1 respectively.
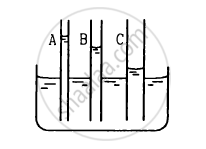
The capillaries shown in figure have inner radii 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm respectively. The liquid in the beaker is water. Find the heights of water level in the capillaries. The surface tension of water is 7.5 × 10−2 N m−1.
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A cubical metal block of edge 12 cm floats in mercury with one fifth of the height inside the mercury. Water in it. Find the height of the water column to be poured.
Specific gravity of mercury = 13.6.
Insect moves over the surface of water because of ______.
The water droplets are spherical in free fall due to ______
Water rises to a height of 20 mm in a capillary tube. If the radius made 1/3rd of its previous value, to what height will the water now rise in the tube?
Mention the S.I unit and dimension of surface tension.
What do you mean by capillarity or capillary action?
If the surface tension of a soap solution is 3 × 10-2 N/m then the work done in forming a soap film of 20 cm × 5 cm will be ______.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'r' coalesce to form a big drop of radius 'R'. The energy released in the process in converted into kinetic energy of the big drop. The speed of the big drop is ______. (T = surface tension of liquid, p = density of liquid)
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
What is surface tension? Explain the applications of surface tension.
The surface tension of soap solution is 25 × 10-3 Nm-1. The excess of pressure inside a soap bubble of diameter 1 cm is ______.
