Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
|
Nucleophilic Substitution: Influences of solvent polarity: The reaction rate (SN2) of 2-bromopropane and NaOH in ethanol containing 40% water is twice slower than in absolute ethanol. Hence the level of solvent polarity has an influence on both SN1 and SN2 reactions but with different results. Generally speaking, a weak polar solvent is favourable for SN2 reaction, while a strong polar solvent is favourable for SN1. Generally speaking, the substitution reaction of tertiary haloalkane is based on SN1 mechanism in solvents with a strong polarity (for example ethanol containing water). |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why racemisation occurs in SN1? (1)
(b) Why is ethanol less polar than water? (1)
(c) Which one of, the following in each pair is more reactive towards SN2 reaction? (2)
(i) CH3 – CH2 – I or CH3CH2 – Cl
(ii)
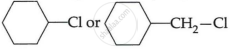
OR
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards SN1 reactions: (2)
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-pentane, 2-Bromo-pentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3- methylbutane
उत्तर
(a) Because the carbocation intermediate generated in SN1 reactions is a planar molecule, it will lead to the formation of d- and l-form products. As a result, racemisation occurs.
(b) Because water has two hydrogen atoms bonded to oxygen \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{O}\\/\backslash\\\ce{[H\phantom{..}H]}
\end{array}\] while alcohol, like ethanol, has a hydrogen atom and alkyl [ethyl] group bonded to an oxygen.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{O}\phantom{.............}\\
\phantom{}/\phantom{.}\backslash\phantom{.............}\\
\ce{H\phantom{...}C2H5 [Ethanol]}
\end{array}\]
(c) (i) CH3 – CH2 – I undergoes SN2 reaction faster than CH3CH2 – Cl.
(ii) The first compound 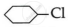 is cyclohexyl chloride [2° halide] and the second compound is cyclohexyl methyl chloride is the primary halide; therefore, in
is cyclohexyl chloride [2° halide] and the second compound is cyclohexyl methyl chloride is the primary halide; therefore, in 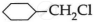 undergoes SN2 reaction faster.
undergoes SN2 reaction faster.
OR
(c) (i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromo-pentane < 1-Bromo-pentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane < 2-Bromo3-methylbutane < 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
moist silver oxide
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be:
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
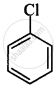
(I)
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
