Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Rahul set up an experiment to find the resistance of aqueous KCl solution for different concentrations at 298 K using a conductivity cell connected to a Wheatstone bridge. He fed the Wheatstone bridge with a.c. power in the audio frequency range 550 to 5000 cycles per second. Once the resistance was calculated from the null point, he also calculated the conductivity K and molar conductivity ∧m and recorded his readings in tabular form. |
| S. No. | Conc. (M) |
k S cm−1 | ∧m S cm2 mol−1 |
| 1. | 1.00 | 111.3 × 10−3 | 111.3 |
| 2. | 0.10 | 12.9 × 10−3 | 129.0 |
| 3. | 0.01 | 1.41 × 10−3 | 141.0 |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why does conductivity decrease with dilution? (1)
(b) If `∧_"m"^0` of KCl is 150.0 S cm2 mol−1, calculate the degree of dissociation of 0.01 M KCI. (1)
(c) If Rahul had used HCl instead of KCl then would you expect the ∧m values to be more or less than those per KCl for a given concentration? Justify. (2)
OR
(c) Amit a classmate of Rahul repeated the same experiment with CH3COOH solution instead of KCl solution. Give one point that would be similar and one that would be different in his observations as compared to Rahul. (2)
उत्तर
(a) The conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of ions in a unit volume of the solution. When a solution is diluted, the number of ions (responsible for carrying current) drops. As a result, solution conductivity diminishes with dilution.
(b) `∧_"m"^0` (KCl) = 150.0 S cm2 mol−1
∧m (0·01 M KCl) = 141 S cm2/mol
As we know
α = `(∧_"m")/(∧_"m"^0)`
= `141/150`
= 0.94
(c) If Rahul had used HCI instead of KCl, the ∧m value for a given concentration would have been greater. The explanation for the increase in molar conductivity of H⊕ over K⊕ is that H⊕ has the maximum molar conductance in an aqueous state because the proton is transported from one water molecule to another in the hydrogen-linked chain of water molecules.
OR
(c) Amit discovered that while molar conductivity improves with dilution, specific conductivity decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define "Molar conductivity".
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
A steady current of 2 amperes was passed through two electrolytic cells X and Y connected in series containing electrolytes FeSO4and ZnSO4 until 2.8g of Fe deposited at the cathode of cell X. How long did the current flow? Calculate the mass of Zn deposited at the cathode of cell Y.
(Molar mass: Fe=56g mol-1,Zn=65.3g mol-1,1F=96500C mol-1)
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 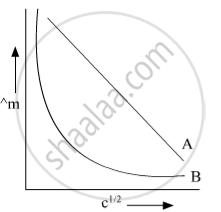
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.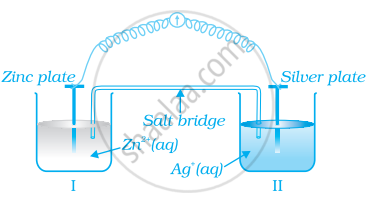
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
Discuss the variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration.
