Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
विकल्प
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
उत्तर
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation:
Molar conductivity increases as concentration lowers. This is because the total volume, V, of a solution containing one mole of electrolyte increases. A drop in 'κ' following the dilution of a solution has been discovered to be more than countered by an increase in volume. The limiting molar conductivity of a solution is its molar conductivity at infinite dilution. In other words, when the electrolyte concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is said to be limiting.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The conductivity of 0.001 mol L-1 solution of CH3COOH is 3.905× 10-5 S cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α) Given λ°(H+)= 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and λ°(CH3COO)= 40.9S cm2mol-1.
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 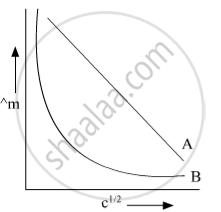
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Assertion: `"E"_("Ag"^+ //"Ag")` increases with increase in concentration of Ag+ ions.
Reason: `"E"_("Ag"^+ //"Ag")` has a positive value.
The limiting molar conductivities for Nacl, KBr and KCI are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. The limiting molar conductivity for Na Br is:-
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
