Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
plot a graph showing the variation of current density (j) versus the electric field (E) for two conductors of different materials. What information from this plot regarding the properties of the conducting material, can be obtained which can be used to select suitable materials for use in making (i) standard resistance and (ii) connecting wires in electric circuits?
उत्तर
The current density j is related to electric field as
E = σ E
Here, σ is the conductivity of the material.
The above relation is equivalent to Ohm’s law.
Now, for a given material, σ is a constant.
Hence, the plot of j versus E will be a straight line starting from the origin.
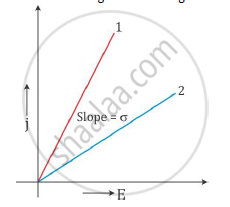
The slope of the graph gives the conductivity σ of the material.
The graph with a greater slope is a better conductor and the graph with a lesser slope is a poor conductor than the other.
(i) To make a standard resistance: A resistor should allow only a limited current to flow through it. Hence, from the graph, we come to know that the material whose plot is similar to plot (2) should be used to make a resistor.
(ii) To make a connecting wire: A wire should allow all the current to flow through it without resisting it. So, it should have a higher conductivity. Hence, from the graph, we come to know that the material whose plot is similar to plot (1) should be used to make a wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that there can be no net charge in a region in which the electric field is uniform at all points.
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E" = ("E"_0 "x")/"l" vec"i".`
Find the charge contained inside the cubical volume bound by the surfaces
x =0, x =a, y=0, y=a, z=0 and z=a. Take
`"E"_0 = 5 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1 , "l" =2 "cm" " and" " a" = 1 "cm" `
The radius of a gold nucleus (Z = 79) is about 7.0 × 10-10 m. Assume that the positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout the nuclear volume. Find the strength of the electric field at (a) the surface of the nucleus and (b) at the middle point of a radius. Remembering that gold is a conductor, is it justified to assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the nucleus and does not come to the outer surface?
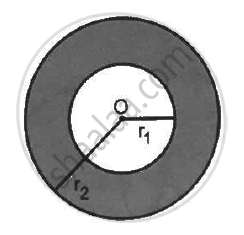
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
The force per unit charge is known as ______.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
