Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
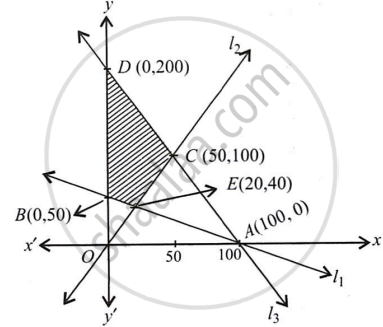
Minimise and Maximise Z = x + 2y
subject to x + 2y ≥ 100, 2x – y ≤ 0, 2x + y ≤ 200; x, y ≥ 0.
उत्तर
The system of constraints is:
x + 2y ≥ 100 ....(i)
2x - y ≤ 0 ....(ii)
2x + y ≤ 200 ....(iii)
and x, y ≥ 0 ....(iv)
Let l1 : x + 2y = 100
l2 : 2x - y = 0
l3 : 2x + y = 200
The shaded region in the figure is the feasible region determined by the system of constraints (i) to (iv).
It is observed that the feasible region ECDB is bounded.
Thus, we use the Corner Point Method to determine the maximum and minimum values of Z.
We have, Z = x + 2y
The co-ordinates of E, C, D and B are (20, 40) (on solving x + 2y = 100 and 2x - y = 0),
(50, 100) (on solving 2x + y = 200 and 2x - y = 0), (0, 200) and (0, 50) respectively.
| Corner Point | Corresponding values of Z |
| (20, 40) | 100 |
| (50, 100) | 250 |
| (0, 200) | 400 (Maximum) |
| (0, 50) | 100 |
Hence Zmax = 400 at (0, 200) and Zmin = 100 at all points on the line segment joining the points (0, 50) and (20, 40).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise Z = – 3x + 4 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Maximise Z = 5x + 3y
subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 15, 5x + 2y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise Z = 3x + 5y
such that x + 3y ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 2, x, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise Z = x + 2y
subject to 2x + y ≥ 3, x + 2y ≥ 6, x, y ≥ 0.
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise Z = 5x + 10 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0, x, y ≥ 0.
Refer to Example 9. How many packets of each food should be used to maximize the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the maximum amount of vitamin A in the diet?
A manufacturer makes two types of toys A and B. Three machines are needed for this purpose and the time (in minutes) required for each toy on the machines is given below:
| Type of toy | Machines | ||
| I | II | III | |
| A | 12 | 18 | 6 |
| B | 6 | 0 | 9 |
Each machine is available for a maximum of 6 hours per day. If the profit on each toy of type A is Rs 7.50 and that on each toy of type B is Rs 5, show that 15 toys of type A and 30 of type B should be manufactured in a day to get maximum profit.
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 200 passengers. A profit of Rs 1000 is made on each executive class ticket and a profit of Rs 600 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves at least 20 seats for executive class. However, at least 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by the executive class. Determine how many tickets of each type must be sold in order to maximize the profit for the airline. What is the maximum profit?
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
Maximise the function Z = 11x + 7y, subject to the constraints: x ≤ 3, y ≤ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
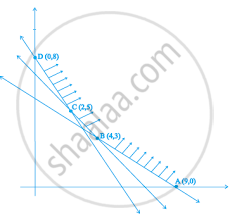
Feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown in Figure. Maximise Z = 5x + 7y.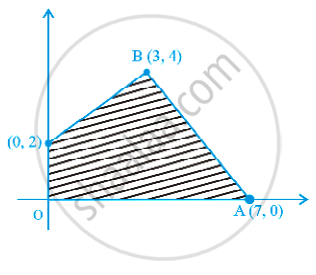
The feasible region for a LPP is shown in figure. Evaluate Z = 4x + y at each of the corner points of this region. Find the minimum value of Z, if it exists.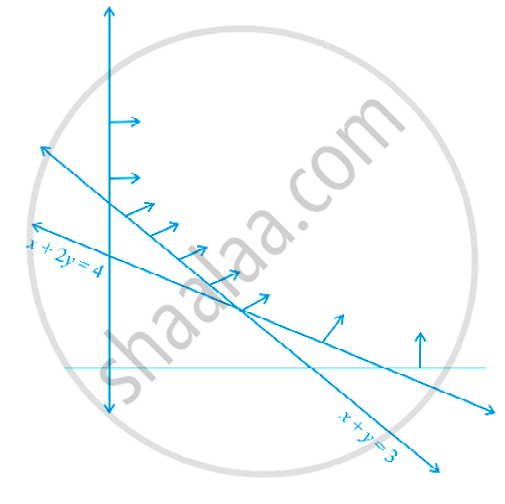
Refer to question 15. Determine the maximum distance that the man can travel.
Maximise Z = x + y subject to x + 4y ≤ 8, 2x + 3y ≤ 12, 3x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
A manufacturer produces two Models of bikes-Model X and Model Y. Model X takes a 6 man-hours to make per unit, while Model Y takes 10 man-hours per unit. There is a total of 450 man-hour available per week. Handling and Marketing costs are Rs 2000 and Rs 1000 per unit for Models X and Y respectively. The total funds available for these purposes are Rs 80,000 per week. Profits per unit for Models X and Y are Rs 1000 and Rs 500, respectively. How many bikes of each model should the manufacturer produce so as to yield a maximum profit? Find the maximum profit.
Refer to Question 27. (Maximum value of Z + Minimum value of Z) is equal to ______.
In a LPP, the objective function is always ______.
If the feasible region for a LPP is ______ then the optimal value of the objective function Z = ax + by may or may not exist.
In a LPP if the objective function Z = ax + by has the same maximum value on two corner points of the feasible region, then every point on the line segment joining these two points give the same ______ value.
A feasible region of a system of linear inequalities is said to be ______ if it can be enclosed within a circle.
A corner point of a feasible region is a point in the region which is the ______ of two boundary lines.
Maximum value of the objective function Z = ax + by in a LPP always occurs at only one corner point of the feasible region.
In a LPP, the minimum value of the objective function Z = ax + by is always 0 if the origin is one of the corner point of the feasible region.
A linear programming problem is as follows:
Minimize Z = 30x + 50y
Subject to the constraints: 3x + 5y ≥ 15, 2x + 3y ≤ 18, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
In the feasible region, the minimum value of Z occurs at:
For an objective function Z = ax + by, where a, b > 0; the corner points of the feasible region determined by a set of constraints (linear inequalities) are (0, 20), (10, 10), (30, 30) and (0, 40). The condition on a and b such that the maximum Z occurs at both the points (30, 30) and (0, 40) is:
In a linear programming problem, the constraints on the decision variables x and y are x − 3y ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3. The feasible region:
Objective function of a linear programming problem is ____________.
The maximum value of the object function Z = 5x + 10 y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x - 2y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ____________.
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem, one finds the feasible region of the linear programming problem, determines its corner points, and evaluates the objective function Z = ax + by at each corner point. If M and m respectively be the largest and smallest values at corner points then ____________.
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem, one finds the feasible region of the linear programming problem, determines its corner points, and evaluates the objective function Z = ax + by at each corner point. Let M and m respectively be the largest and smallest values at corner points. In case feasible region is unbounded, M is the maximum value of the objective function if ____________.
If two corner points of the feasible region are both optimal solutions of the same type, i.e., both produce the same maximum or minimum.
Maximize Z = 6x + 4y, subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 10 x1 + 25 x2, subject to 0 ≤ x1 ≤ 3, 0 ≤ x2 ≤ 3, x1 + x2 ≤ 5.
The feasible region for an LPP is shown shaded in the following figure. Minimum of Z = 4x + 3y occurs at the point.