Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The cost of 2 books, 6 notebooks and 3 pens is Rs 40. The cost of 3 books, 4 notebooks and 2 pens is Rs 35, while the cost of 5 books, 7 notebooks and 4 pens is Rs 61. Using this information and matrix method, find the cost of 1 book, 1 notebook and 1 pen separately.
उत्तर
Let the cost of 1 book, 1 notebook and 1 pen be Rs x, Rs y and Rs z respectively.
According to the given conditions,
2x + 6y + 3z = 40
3x + 4y + 2z = 35
5x + 7y + 4z = 61
These equations can be written in the matrix form as

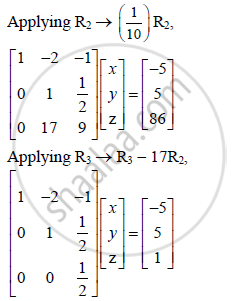
By equality of matrices,\
x − 2y − z = −5 ….(i)
y + z/2= 5 ….(ii)
z/2 = 1 ….(iii)
From (iii), z = 2
Putting z = 2 in (ii), we get
y + 1 = 5
∴ y = 4
Putting y = 4, z = 2 in (i), we get
x − 8 − 2 = − 5
∴ x = 5
Thus, the cost of 1 book, 1 notebook and 1 pen are 5, 4 and 2 respectively
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The cost of 4 pencils, 3 pens and 2 erasers is Rs. 60. The cost of 2 pencils, 4 pens and 6 erasers is Rs. 90 whereas the cost of 6 pencils, 2 pens and 3 erasers is Rs. 70. Find the cost of each item by using matrices.
Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of the matrix A = `((8,4,3),(2,1,1),(1,2,2))`and use it to solve the following system of linear equations :
8x + 4y + 3z = 19
2x + y + z = 5
x + 2y + 2z = 7
Prove that :
In the following matrix equation use elementary operation R2 → R2 + R1 and the equation thus obtained:
Use elementary column operation C2 → C2 + 2C1 in the following matrix equation : \[\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 0\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}3 & 1 \\ 2 & 0\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 \\ - 1 & 1\end{bmatrix}\]
Use elementary column operations \[C_2 \to C_2 - 2 C_1\] in the matrix equation \[\begin{pmatrix}4 & 2 \\ 3 & 3\end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}1 & 2 \\ 0 & 3\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}2 & 0 \\ 1 & 1\end{pmatrix}\] .
Apply the given elementary transformation on each of the following matrices `[(2, 4),(1, -5)]`, C1 ↔ C2.
Transform `[(1, -1, 2),(2, 1, 3),(3, 2, 4)]` into an upper traingular matrix by suitable row transformations.
Find the cofactor matrix, of the following matrices: `[(5, 8, 7),(-1, -2, 1),(-2, 1, 1)]`
Find the adjoint of the following matrices : `[(1, -1, 2),(-2, 3, 5),(-2, 0, -1)]`
Choose the correct alternative.
If A = `[("a", 0, 0),(0, "a", 0),(0, 0,"a")]`, then |adj.A| = _______
Fill in the blank :
Order of matrix `[(2, 1, 1),(5, 1, 8)]` is _______
Solve the following :
If A = `[(1, 0, 0),(2, 1, 0),(3, 3, 1)]`, the reduce it to unit matrix by using row transformations.
If three numbers are added, their sum is 2. If 2 times the second number is subtracted from the sum of first and third numbers, we get 8. If three times the first number is added to the sum of second and third numbers, we get 4. Find the numbers using matrices.
Matrix `[("a", "b", "c"),("p", "q", "r"),(2"a" - "p", 2"b" - "q", 2"c" - "r")]` is a singular
If A is a 3 × 3 matrix and |A| = 2, then the matrix represented by A (adj A) is equal to.
If `[(1, 0, -1),(0, 2, 1),(1, -2, 0)] [(x),(y),(z)] = [(1),(2),(3)]`, then the values of x, y, z respectively are ______.
The inverse of a symmetric matrix is ______.
Find the matrix A satisfying the matrix equation:
`[(2, 1),(3, 2)] "A" [(-3, 2),(5, -3)] = [(1, 0),(0, 1)]`
If possible, find BA and AB, where A = `[(2, 1, 2),(1, 2, 4)]`, B = `[(4, 1),(2, 3),(1, 2)]`
If P = `[(x, 0, 0),(0, y, 0),(0, 0, z)]` and Q = `[("a", 0, 0),(0, "b", 0),(0, 0, "c")]`, prove that PQ = `[(x"a", 0, 0),(0, y"b", 0),(0, 0, z"c")]` = QP
If `[(xy, 4),(z + 6, x + y)] = [(8, w),(0, 6)]`, then find values of x, y, z and w.
If A = `[(1, 5),(7, 12)]` and B `[(9, 1),(7, 8)]`, find a matrix C such that 3A + 5B + 2C is a null matrix.
If P(x) = `[(cosx, sinx),(-sinx, cosx)]`, then show that P(x) . (y) = P(x + y) = P(y) . P(x)
If possible, using elementary row transformations, find the inverse of the following matrices
`[(2, 3, -3),(-1, 2, 2),(1, 1, -1)]`
If possible, using elementary row transformations, find the inverse of the following matrices
`[(2, 0, -1),(5, 1, 0),(0, 1, 3)]`
If A = `1/pi [(sin^-1(xpi), tan^-1(x/pi)),(sin^-1(x/pi), cot^-1(pix))]`, B = `1/pi [(-cos^-1(x/pi), tan^-1 (x/pi)),(sin^-1(x/pi),-tan^-1(pix))]`, then A – B is equal to ______.
On using elementary column operations C2 → C2 – 2C1 in the following matrix equation `[(1, -3),(2, 4)] = [(1, -1),(0, 1)] [(3, 1),(2, 4)]`, we have: ______.
In applying one or more row operations while finding A–1 by elementary row operations, we obtain all zeros in one or more, then A–1 ______.
A matrix denotes a number.
Two matrices are equal if they have same number of rows and same number of columns.
`abs((1,1,1),("e",0,sqrt2),(2,2,2))` is equal to ____________.
If f(x) = `|(1 + sin^2x, cos^2x, 4 sin 2x),(sin^2x, 1 + cos^2x, 4 sin 2x),(sin^2 x, cos^2 x, 1 + 4 sin 2x)|`
What is the maximum value of f(x)?
if `A = [(2,5),(1,3)] "then" A^-1` = ______
