Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge 0.4 μC due to another small sphere of charge − 0.8 μC in air is 0.2 N.
- What is the distance between the two spheres?
- What is the force on the second sphere due to the first?
उत्तर
(a) Electrostatic force on the first sphere, F = 0.2 N
Charge on this sphere, q1 = 0.4 μC = 0.4 × 10−6 C
Charge on the second sphere, q2 = − 0.8 μC = − 0.8 × 10−6 C
Electrostatic force between the spheres is given by the relation,
`F=(q_1q_2)/(4piin_0r^2)` and , `1/(4piin_0)`
= `9xx10^9 Nm^2C^-2`
Where, ∈0 = Permittivity of free space
`r^2=(q_1q_2)/(4piin_0F)`
`= (9xx10^9xx0.4xx10^-6xx0.8xx10^-6)/0.2`
`=144xx10^-4`
`r=sqrt(144xx10^-4)`
= 0.12 m
The distance between the two spheres is 0.12 m.
(b) Both the spheres attract each other with the same force. Therefore, the force on the second sphere due to the first is 0.2 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
- Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centers separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 × 10−7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.
- What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?
Suppose that the particle is an electron projected with velocity vx = 2.0 × 106 m s−1. If E between the plates separated by 0.5 cm is 9.1 × 102 N/C, where will the electron strike the upper plate? (|e| = 1.6 × 10−19 C, me = 9.1 × 10−31 kg)
Three-point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 'l' as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q

(b) Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite distance.
Does the force on a charge due to another charge depend on the charges present nearby?
A hydrogen atom contains one proton and one electron. It may be assumed that the electron revolves in a circle of radius 0.53 angstrom (1 angstrom = 10−10 m and is abbreviated as Å ) with the proton at the centre. The hydrogen atom is said to be in the ground state in this case. Find the magnitude of the electric force between the proton and the electron of a hydrogen atom in its ground state.
Two small spheres, each with a mass of 20 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of length 40 cm each. The spheres are identically charged and the separation between the balls at equilibrium is found to be 4 cm. Find the charge on each sphere.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C is held fixed on a horizontal table. A second charged particle of mass 80 g stays in equilibrium on the table at a distance of 10 cm from the first charge. The coefficient of friction between the table and this second particle is μ = 0.2. Find the range within which the charge of this second particle may lie.
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. If it is displaced through a distance x perpendicular to AB, what would be the electric force experienced by it?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Under what conditions will the particle C execute simple harmonic motion if it is released after such a small displacement? Find the time period of the oscillations if these conditions are satisfied.
A point charge produces an electric field of magnitude 5.0 NC−1 at a distance of 40 cm from it. What is the magnitude of the charge?
Three identical charges, each with a value of 1.0 × 10−8 C, are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 20 cm. Find the electric field and potential at the centre of the triangle.
Two equal charges, 2.0 × 10−7 C each, are held fixed at a separation of 20 cm. A third charge of equal magnitude is placed midway between the two charges. It is now moved to a point 20 cm from both the charges. How much work is done by the electric field during the process?
Two positive charges ______.
For charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance R the magnitude of the electrostatic force is given by ______.
A charge Q is divided into two parts of q and Q – q. If the coulomb repulsion between them when they are separated is to be maximum, the ratio of Q/q should be ______.
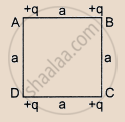
Four equal charges q are placed at the four comers A, B, C, D of a square of length a. The magnitude of the force on the charge at B will be ______.
A spring of spring constant 5 × 103 N/m is stretched initially by 5 cm from the unstretched position. Then the work required to stretch it further by another 5 cm is:
The ratio of the forces between two charges placed at a certain distance apart in the air and by the same distance apart in a medium of dielectric constant K is ______.
Two point charges +2 C and +6 C repel each other with a force of 12 N. If a charge of -4 C is given to each of these charges, then the force now is ______.
What is meant by the statement: "Relative permittivity of water is 81"?
