Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The equation of one side of an equilateral triangle is x − y = 0 and one vertex is \[(2 + \sqrt{3}, 5)\]. Prove that a second side is \[y + (2 - \sqrt{3}) x = 6\] and find the equation of the third side.
उत्तर
Let
\[A\left( 2 + \sqrt{3}, 5 \right)\] be the vertex of the equilateral triangle ABC and x − y = 0 be the equation of BC.
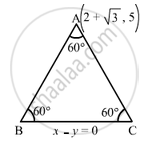
Here, we have to find the equations of sides AB and AC, each of which makes an angle of
\[{60}^\circ\] with the line x − y = 0
We know the equations of two lines passing through a point \[\left( x_1 , y_1 \right)\] and making an angle \[\alpha\] with the line whose slope is m.
\[y - y_1 = \frac{m \pm \tan\alpha}{1 \mp m\tan\alpha}\left( x - x_1 \right)\]
Here,
\[x_1 = 2 + \sqrt{3}, y_1 = 5, \alpha = {60}^\circ , m = 1\]
So, the equations of the required sides are
\[y - 5 = \frac{1 + \tan {60}^\circ}{1 - \tan {60}^\circ}\left( x - 2 - \sqrt{3} \right) \text { and }y - 5 = \frac{1 - \tan {60}^\circ}{1 + \tan {60}^\circ}\left( x - 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - 5 = - \left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)\left( x - 2 - \sqrt{3} \right) \text { and } y - 5 = - \left( 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)\left( x - 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - 5 = - \left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)x + \left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)^2 \text { and } y - 5 = - \left( 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)x + \left( 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)\left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)x + y = 2 + 4\sqrt{3} \text { and } \left( 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)x + y - 6 = 0\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the equation of the line parallel to x-axis and passing through (3, −5).
Find the equation of the line parallel to x-axis and having intercept − 2 on y-axis.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (6, 2) and having slope − 3.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through (−2, 3) and inclined at an angle of 45° with the x-axis.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through (3, −2) and making an angle of 60° with the positive direction of y-axis.
Prove that the perpendicular drawn from the point (4, 1) on the join of (2, −1) and (6, 5) divides it in the ratio 5 : 8.
Find the equations to the altitudes of the triangle whose angular points are A (2, −2), B (1, 1) and C (−1, 0).
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the following pair of point :
(0, −a) and (b, 0)
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the following pair of point :
(a, b) and (a + b, a − b)
Find the equations of the sides of the triangles the coordinates of whose angular point is respectively (0, 1), (2, 0) and (−1, −2).
Find the equations of the medians of a triangle, the coordinates of whose vertices are (−1, 6), (−3, −9) and (5, −8).
Find the equation to the straight line which bisects the distance between the points (a, b), (a', b') and also bisects the distance between the points (−a, b) and (a', −b').
The vertices of a quadrilateral are A (−2, 6), B (1, 2), C (10, 4) and D (7, 8). Find the equation of its diagonals.
Find the equation to the straight line cutting off intercepts 3 and 2 from the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through (1, −2) and cuts off equal intercepts on the axes.
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (2, 2) and cutting off intercepts on the axes whose sum is 9.
Find the equations of the straight lines which pass through the origin and trisect the portion of the straight line 2x + 3y = 6 which is intercepted between the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (2, 1) and bisecting the portion of the straight line 3x − 5y = 15 lying between the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the origin and bisecting the portion of the line ax + by + c = 0 intercepted between the coordinate axes.
A line is such that its segment between the straight lines 5x − y − 4 = 0 and 3x + 4y − 4 = 0 is bisected at the point (1, 5). Obtain its equation.
Find the equation of straight line passing through (−2, −7) and having an intercept of length 3 between the straight lines 4x + 3y = 12 and 4x + 3y = 3.
Three sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC are 5x − 3y + 2 = 0, x − 3y − 2 = 0 and x + y − 6 = 0 respectively. Find the equation of the altitude through the vertex A.
Find the equation of a line passing through the point (2, 3) and parallel to the line 3x − 4y + 5 = 0.
Find the equation of a line passing through (3, −2) and perpendicular to the line x − 3y + 5 = 0.
Find the distance of the point (1, 2) from the straight line with slope 5 and passing through the point of intersection of x + 2y = 5 and x − 3y = 7.
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the origin and making an angle of 45° with the straight line \[\sqrt{3}x + y = 11\].
Find the equations of the two straight lines through (1, 2) forming two sides of a square of which 4x+ 7y = 12 is one diagonal.
Show that the straight lines given by (2 + k) x + (1 + k) y = 5 + 7k for different values of k pass through a fixed point. Also, find that point.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point of intersection of the lines 3x − y = 5 and x + 3y = 1 and makes equal and positive intercepts on the axes.
Find the equations of the lines through the point of intersection of the lines x − 3y + 1 = 0 and 2x + 5y − 9 = 0 and whose distance from the origin is \[\sqrt{5}\].
Write the integral values of m for which the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the lines y = mx + 1 and 3x + 4y = 9 is an integer.
If a, b, c are in A.P., then the line ax + by + c = 0 passes through a fixed point. Write the coordinates of that point.
A line passes through the point (2, 2) and is perpendicular to the line 3x + y = 3. Its y-intercept is
In what direction should a line be drawn through the point (1, 2) so that its point of intersection with the line x + y = 4 is at a distance `sqrt(6)/3` from the given point.
A straight line moves so that the sum of the reciprocals of its intercepts made on axes is constant. Show that the line passes through a fixed point.
If a, b, c are in A.P., then the straight lines ax + by + c = 0 will always pass through ______.
