Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The latent heat of vaporisation is a term referred for the conversion of gas into liquid.
विकल्प
Right
Wrong
उत्तर
The latent heat of vaporisation is a term referred for the conversion of gas into liquid- Wrong
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
Explain the following:
The surrounding become pleasantly warm when water in a lake starts freezing in cold countries.
The specific latent heat of fusion of water is ______.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to convert 100 g of ice at −10℃ completely into water at 100℃. Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1 K-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1K-1, specific latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1.
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
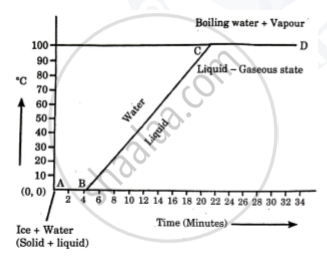
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
A substance changes from its solid state to the liquid state when heat is supplied to it. What name is given to heat absorbed by the substance.
Explain the statement; “The specific latent heat of vaporization of wafer is 2260 × 103 J/kg”.
Why does evaporation causes cooling and why is water used in hot water bottles?
What observation you will record and how will you determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice?
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
1 kg of dry air at a temperature of 40 °C can hold a maximum of 49 g of water vapour.
2875 J of heat is required to melt 115 g of lead at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat capacity of fusion of lead.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to melt 200 g of ice at 0°C to water at 100°C. (Specific latent heat of ice = 336 Jg-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg-1 °C-1)
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
20 g of ice at 0°C absorbs 10,920 J of heat energy to melt and change to water at 50°C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1 K-1.
