Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to melt 200 g of ice at 0°C to water at 100°C. (Specific latent heat of ice = 336 Jg-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg-1 °C-1)
उत्तर
200 g of ice at 0°C
Q1 = mLf
200 g of H2O at 0°C
Q2 = m × c × θR
200 g of H2O at 100°C
Total heat required
Q = Q1 + Q2
= mLf + m × c × θR
= (200 × 336) + (200 × 4·2 × 100)
= (67200) + (84000)
= 1,51,200 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any two measures to minimize the impact of global warming.
Explain the following:
The surrounding become pleasantly warm when water in a lake starts freezing in cold countries.
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is ______.
Define the following terms:
(i) Latent heat,
(ii) Latent heat of fusion of ice.
Define specific latent heat of vaporization of a substance.
Explain why water is used in hot water bottles for fomentation and also as a universal coolant.
Explain the meaning of the term latent heat. State its S. I. unit.
What happens to the heat supplied to a substance when the heat supplied causes no change in the temperature of the substance?
Why water get cooled in a ‘Surahi’ in hot season?
State two advantages of the high specific latent heat capacity of steam, which is about 226 × 104 J/kg?
Derive an expression for the amount of heat given out or taken up, when its temperature falls or rises by t°C.
What observation you will record and how will you determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice?
When ice is converted into water : constant temperature : : before the water evaporates : _______
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Define boiling point of a liquid.
1 kg of dry air at a temperature of 40 °C can hold a maximum of 49 g of water vapour.
Who introduced the term latent heat?
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
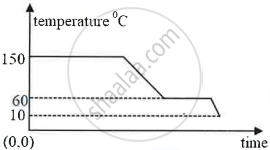
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
