Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The sides of triangle is given below. Determine it is right triangle or not.
a = 9 cm, b = l6 cm and c = 18 cm
उत्तर
We have,
a = 9 cm, b = 16 cm and c = 18 cm
∴ a2 = 81, b2 = 256 and c2 = 324
Since, a2 + b2 = 81 + 256 = 337
≠ c2
Then, by converse of Pythagoras theorem, given triangle is not a right triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Construct a triangle ABC with sides BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 45° and ∠A = 105°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/4` times the corresponding sides of ∆ABC.
A ladder 17 m long reaches a window of a building 15 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the building.
ABCD is a square. F is the mid-point of AB. BE is one third of BC. If the area of ΔFBE = 108 cm2, find the length of AC.
In an isosceles triangle ABC, if AB = AC = 13 cm and the altitude from A on BC is 5 cm, find BC.
In right-angled triangle ABC in which ∠C = 90°, if D is the mid-point of BC, prove that AB2 = 4AD2 − 3AC2.
Determine whether the triangle having sides (a − 1) cm, 2`sqrta` cm and (a + 1) cm is a right-angled
triangle.
State the converse of Pythagoras theorem.
In an equilateral triangle with side a, prove that area = `sqrt3/4` 𝑎2
The co-ordinates of the points A, B and C are (6, 3), (−3, 5) and (4, −2) respectively. P(x, y) is any point in the plane. Show that \[\frac{ar\left( ∆ PBC \right)}{ar\left( ∆ ABC \right)} = \left| \frac{x + y - 2}{7} \right|\]
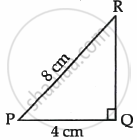
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right triangle right angled at Q. If PQ = 4 cm and PR = 8 cm, then P is ______.