Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two line segments 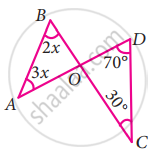
उत्तर
In ∆AOB and ∆DOC,
∠AOB = ∠DOC ...[∵ Vertically opposite angles are equal]
Let ∠AOB = ∠DOC = y
By angle sum property of a triangle we have
∠A + ∠B + ∠AOB = ∠D + ∠C + ∠DOC = 180°
3x + 2x + y = 70° + 30° + y = 180°
5x + y = 100° + y = 180°
Here 5x + y = 100° + y
5x = 100° + y – y
5x = 100°
x =
∠A = 3x = 3 × 20 = 60°
∠B = 2x = 2 × 20 = 40°
∠A = 60°
∠B = 40°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
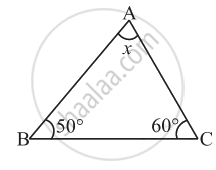
Find the value of the unknown x in the following diagram:
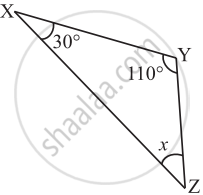
Find the value of the unknown x in the given diagram:
In a right angled triangle ABC, ∠B is right angle, ∠A is x + 1 and ∠C is 2x + 5. Find ∠A and ∠C
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. Find the angles of the triangle.
A triangle ABC is right angled at A. L is a point on BC such that AL ⊥ BC. Prove that ∠BAL = ∠ACB.
In an isosceles triangle, one angle is 70°. The other two angles are of ______.
- 55° and 55°
- 70° and 40°
- any measure
In the given option(s) which of the above statement(s) are true?
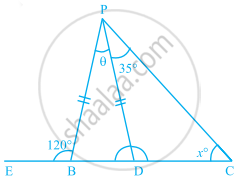
In the given figure, PB = PD. The value of x is ______.
In ∆ABC, ∠Α = 100°, AD bisects ∠A and AD ⊥ BC. Then, ∠B is equal to ______.
By which of the following criterion two triangles cannot be proved congruent?
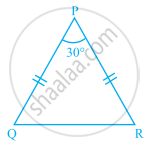
In ΔPQR of the given figure, PQ = PR. Find the measures of ∠Q and ∠R.