Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two pendulums with identical bobs and lengths are suspended from a common support such that in rest position the two bobs are in contact (Figure). One of the bobs is released after being displaced by 10° so that it collides elastically head-on with the other bob.

- Describe the motion of two bobs.
- Draw a graph showing variation in energy of either pendulum with time, for 0 ≤ t ≤ 2T, where T is the period of each pendulum.
उत्तर
a. Consider the adjacent diagram in which the bob B is displaced through an angle θ and released.
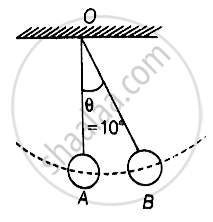
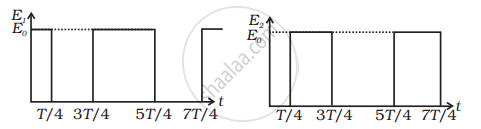
At t = 0, suppose bob B is displaced by θ = 10° to the right. It is given potential energy E1 = E. Energy of A, E2 = 0
When B is released, it strikes A at t = T/4. In the head-on elastic collision between B and A comes to rest and A gets the velocity of B. Therefore. E1 = 0 and E2 = E. At t = 27T/4, B reaches its extreme right position when KE of A is converted into PE = E2 = E. Energy of B, E1 = 0.
At t = 3T/4, A reaches its mean position. when its PE is converted into KE = E2 = E. It collides elastically with B and transfers the whole of its energy to B. Thus, E2 = 0 and E1 = E. The entire process is repeated.
b. The values of energies of B and A at different time intervals are tabulated here. The plot of energy with time 0 ≤ t ≤ 2T is shown separately for 8 and A in the figure below.
| Time (t) | Energy of A (E1) |
Energy of B (E2) |
| 0 | E | 0 |
| T/4 | 0 | E |
| 2T/4 | 0 | E |
| 3T/4 | E | 0 |
| 4T/4 | E | 0 |
| 5T/4 | 0 | E |
| 6T/4 | 0 | E |
| 7T/4 | E | 0 |
| 8T/4 | E | 0 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
A bullet of mass 0.012 kg and horizontal speed 70 m s–1 strikes a block of wood of mass 0.4 kg and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block.
A mass M moving with velocity 'v' along x-axis collides and sticks to another mass 2M which is moving along Y-axis with velocity 3v. After collision, the velocity of the combination is ______.
A body of mas 'm' moving with speed 3 m/s collides with a body of mass '2m' at rest. The coalesced mass will start to move with a speed of ______.
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for head-on collision, both the balls move forward.
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
An alpha-particle of mass m suffers 1-dimensional elastic collision with a nucleus at rest of unknown mass. It is scattered directly backwards losing, 64% of its initial kinetic energy. The mass of the nucleus is ______.
A sphere of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v' collides head-on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is ______. ( e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
Three identical blocks A, B and C are placed on horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks A and C are at rest. But A is approaching towards B with a speed 10 m/s. The coefficient of restitution for all collision is 0.5. The speed of the block C just after the collision is ______.

Answer carefully, with reason:
Is the total linear momentum conserved during the short time of an inelastic collision of two balls ?
