Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction takes place:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......................}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{......................}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH3 ->[HBr] CH3 - C - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{...................}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
Give a mechanism for this reaction.
(Hint: The secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more
stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom.)
उत्तर
The described reaction is an example of carbocation rearrangement that occurs via hydride shift. The mechanism for it is –
Step 1: Formation of carbocation: Protonation of alcohol.
\[\ce{HBr -> H+ + B\overset{—}{r}}\]
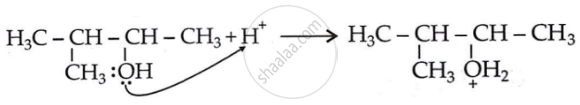
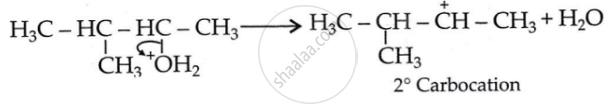
Step 2: 1, 2-hydride shift: Formation of a more stable, 3° carbocation.
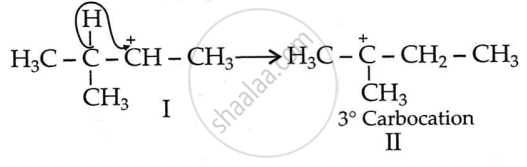
Initially, a 2° carbocation (I) was produced. However, the more stable 3° counterpart causes a hydride shift, forming the more stable carbocation (II).
Step 3: Attack of nucleophile: Generation of product.
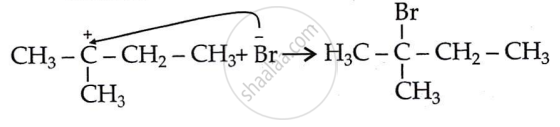
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to aldehyde.
Write the mechanism (using curved arrow notation) of the following reaction :
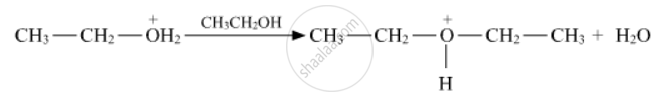
Lucas test is used for the detection of _____________.
In the reduction \[\ce{R - CHO + H2 -> RCH2OH}\] the catalyst used is:
By which of the following methods alcohol can be prepared in excellent yield?
Lucas test is done to differentiate between ____________.
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is:
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH}\] can be converted into \[\ce{CH3CHO}\] by ______.
Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Di-tert-butyl ether can’t be prepared by this method. Explain.
The correct geometry around oxygen in CH3OCH3 is
Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation?
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
