Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction takes place:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......................}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{......................}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH3 ->[HBr] CH3 - C - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{...................}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
Give a mechanism for this reaction.
(Hint: The secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more
stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom.)
उत्तर
The described reaction is an example of carbocation rearrangement that occurs via hydride shift. The mechanism for it is –
Step 1: Formation of carbocation: Protonation of alcohol.
\[\ce{HBr -> H+ + B\overset{—}{r}}\]
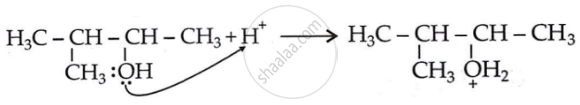
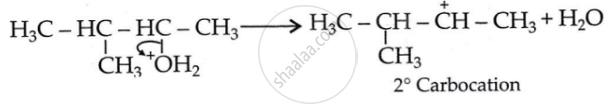
Step 2: 1, 2-hydride shift: Formation of a more stable, 3° carbocation.
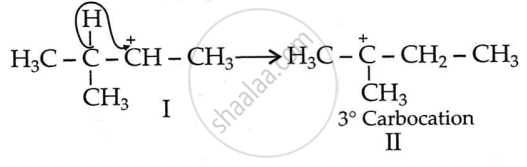
Initially, a 2° carbocation (I) was produced. However, the more stable 3° counterpart causes a hydride shift, forming the more stable carbocation (II).
Step 3: Attack of nucleophile: Generation of product.
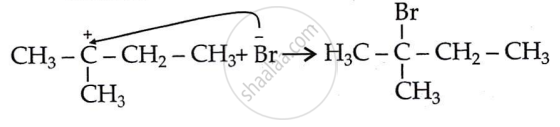
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mechanism of the following reaction :
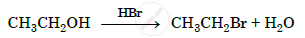
Ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
Show how will you synthesize pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Dilute HNO3 with phenol.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
By which of the following methods alcohol can be prepared in excellent yield?
Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH?
(i) H2/Pd
(ii) LiAlH4
(iii) NaBH4
(iv) Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
Lucas test is done to differentiate between ____________.
Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone?
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves ______.
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Explain why nucleophilic substitution reactions are not very common in phenols.
In Kolbe’s reaction, instead of phenol, phenoxide ion is treated with carbon dioxide. Why?
What is Lucas reagent?
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
