Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to figure of a cube of edge a and mass m, state whether the following are true or false. (O is the centre of the cube.)
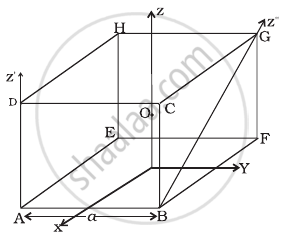
- The moment of inertia of cube about z-axis is Iz = Ix + Iy
- The moment of inertia of cube about z ′ is I'z = `I_z + (ma^2)/2`
- The moment of inertia of cube about z″ is = `I_z + (ma^2)/2`
- Ix = Iy
उत्तर
a, b and d
Explanation:
a. Theorem of perpendicular axes is applicable only for laminar (plane) objects. Thus. option (a) is false.
b. As z' || z and distance between them = `a sqrt(2)/2 = a/sqrt(2)`
Now, by the theorem of parallel axes
`I_z = I_z + m(a/sqrt(2))^2 = I_z + (ma^2)/2`
Hence, choice (b) is true.
c. z is not parallel to z hence, the theorem of parallel axis cannot be applied. Thus, option (c) is false.
d. As x and y-axes are symmetrical.
Hence, Ix = Iy
Thus, option (d) is true.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30°. At the bottom of the inclined plane, the centre of mass of the cylinder has a speed of 5 m/s.
(a) How far will the cylinder go up the plane?
(b) How long will it take to return to the bottom?
Let I1 an I2 be the moments of inertia of two bodies of identical geometrical shape, the first made of aluminium and the second of iron.
Suppose the smaller pulley of the previous problem has its radius 5⋅0 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅10 kg-m2. Find the tension in the part of the string joining the pulleys.
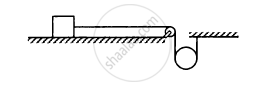
The descending pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2. The fixed pulley is light and the horizontal plane frictionless. Find the acceleration of the block if its mass is 1⋅0 kg.
Four bodies of masses 2 kg, 3 kg, 4 kg and 5 kg are placed at points A, B, C, and D respectively of a square ABCD of side 1 metre. The radius of gyration of the system about an axis passing through A and perpendicular to plane is
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2 ’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
Consider a badminton racket with length scales as shown in the figure.
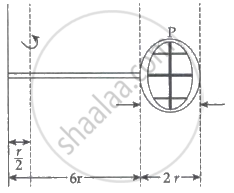
If the mass of the linear and circular portions of the badminton racket is the same (M) and the mass of the threads is negligible, the moment of inertia of the racket about an axis perpendicular to the handle and in the plane of the ring at, `r/2` distance from the ends A of the handle will be ______ Mr2.
