Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to figure of a cube of edge a and mass m, state whether the following are true or false. (O is the centre of the cube.)
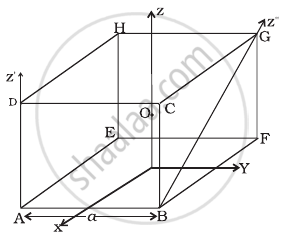
- The moment of inertia of cube about z-axis is Iz = Ix + Iy
- The moment of inertia of cube about z ′ is I'z = `I_z + (ma^2)/2`
- The moment of inertia of cube about z″ is = `I_z + (ma^2)/2`
- Ix = Iy
उत्तर
a, b and d
Explanation:
a. Theorem of perpendicular axes is applicable only for laminar (plane) objects. Thus. option (a) is false.
b. As z' || z and distance between them = `a sqrt(2)/2 = a/sqrt(2)`
Now, by the theorem of parallel axes
`I_z = I_z + m(a/sqrt(2))^2 = I_z + (ma^2)/2`
Hence, choice (b) is true.
c. z is not parallel to z hence, the theorem of parallel axis cannot be applied. Thus, option (c) is false.
d. As x and y-axes are symmetrical.
Hence, Ix = Iy
Thus, option (d) is true.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time?
Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time?
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
Let I1 an I2 be the moments of inertia of two bodies of identical geometrical shape, the first made of aluminium and the second of iron.
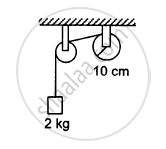
A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2 and radius 10 cm and goes through a light pulley to support a block of mass 2⋅0 kg as shown in the following figure. Find the acceleration of the block.
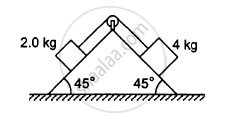
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅5 kg-m2about its axis. Assuming the inclined planes to be frictionless, calculate the acceleration of the 4⋅0 kg block.
A diver having a moment of inertia of 6⋅0 kg-m2 about an axis thorough its centre of mass rotates at an angular speed of 2 rad/s about this axis. If he folds his hands and feet to decrease the moment of inertia to 5⋅0 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
Two blocks of masses 400 g and 200 g are connected through a light string going over a pulley which is free to rotate about its axis. The pulley has a moment of inertia \[1 \cdot 6 \times {10}^{- 4} kg - m^2\] and a radius 2⋅0 cm, Find (a) the kinetic energy of the system as the 400 g block falls through 50 cm, (b) the speed of the blocks at this instant.
Why does a solid sphere have smaller moment of inertia than a hollow cylinder of same mass and radius, about an axis passing through their axes of symmetry?
Moment of inertia (M.I.) of four bodies, having same mass and radius, are reported as :
I1 = M.I. of thin circular ring about its diameter,
I2 = M.I. of circular disc about an axis perpendicular to disc and going through the centre,
I3 = M.I. of solid cylinder about its axis and
I4 = M.I. of solid sphere about its diameter.
Then -
