Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br.
उत्तर
C4H9Br is a saturated compound because its parent hydrocarbon is C4H10. Its isomers are as follows –
(i) \[\ce{\underset{1-Bromobutane}{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - Br}}\]
(ii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{\underset{2-Bromobutane}{CH3-CH2-CH-CH3}}
\end{array}\]
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\
|\phantom{.......}\\
\ce{\underset{1-Bromo-2-Methylpropane}{CH3-CH-CH2Br}}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - Br}\phantom{.....}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{.}\ce{\underset{2-Bromo-2-Methylpropane}{CH3}}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
Which of the following is an example of SN2 reaction?
Which of the following is a primary halide?
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction?
Most reactive halide towards SN1 reaction is ____________.
An important chemical method to resolve a racemic mixture makes use of the formation of ______.
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify X and Y in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5Br ->[X] Product ->[Y] C3H7NH2}\]
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
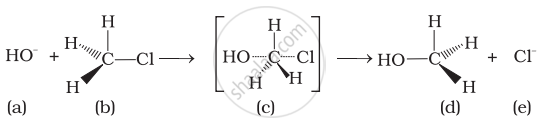
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
How do polar solvents help in the first step in SN1 mechanism?
Among the following compounds I - IV, which one forms a yellow precipitate on reacting sequentially with (i) NaOH (ii) dil. HNO3 (iii) AgNO3?
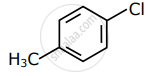 |
 |
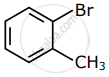 |
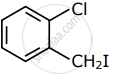 |
| I | II | III | IV |
Racemisation occurs in ______.
Acetic anhydride from acetic acid
